자격 증명 관리 일괄 삭제
업무상 자격증명을 삭제 해야 하는 경우가 발생합니다.
매번 작업 해주기 귀찮아서 확인해보니 한번에 삭제 하는 방법이 있네요
....저걸 하나하나 모두 삭제
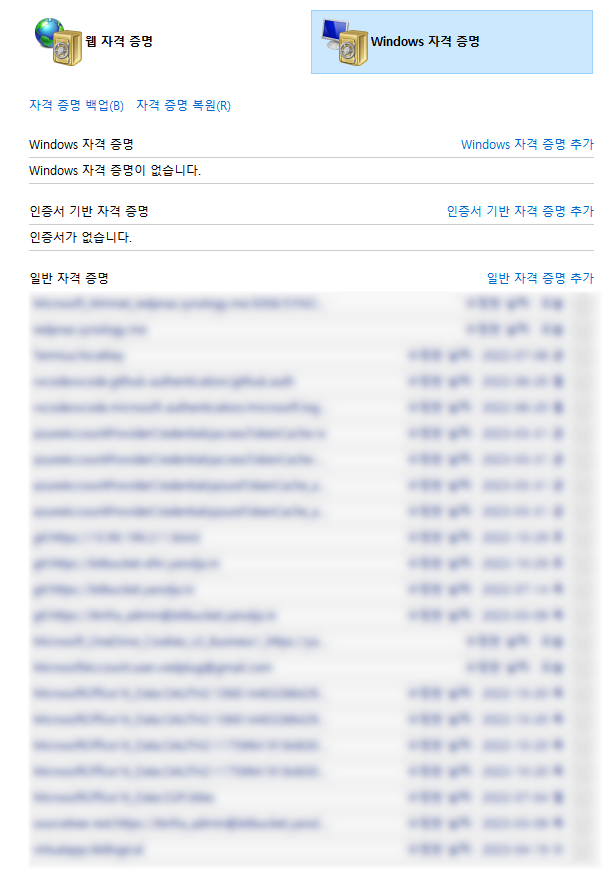
cmdkey로 리스트를 불러올 수 있어서 혹시나 해보았으나...될리가 없죠..
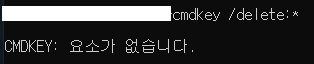
구글링을 해보니 누군가 간단하게 스크립트로 만들어 놓은 것을 확인
$Credentials = (cmdkey /list | Where-Object {$_ -like "*Target=*"})
Foreach ($Target in $Credentials) {
$Target = ($Target -split (":", 2) | Select-Object -Skip 1).substring(1)
$Argument = "/delete:" + $Target
Start-Process Cmdkey -ArgumentList $Argument -NoNewWindow -RedirectStandardOutput $False
}cmdkey에서 리스트를 뽑아서 한땀한땀 삭제를 해주는 스크립트 입니다.

찾아서 파괴파괴!
돌리고 나니... 모두 삭제 확인하였습니다.
[Kubernetes] CKA (Certified Kubernetes Administrator) 취득
안녕하세요 Redplug입니다.
CKA 자격증 취득하였습니다.
CKA시험의 경우 접수 후 1년간 2번의 시험 기회가 제공됩니다. (노쇼일 경우 2번째 시험 기회 박탈)
공부자체는 약 1년 간 진행 하였으며, 쿠버네티스 관련경험은 크게 많지 않은 상태였습니다.
시험은 실습으로 진행하기 때문에 리눅스에 대한 기본적인 지식(쉘 다루는 방법)가 필요하고
시험 자체는 하기 과정 진행할 경우에 어렵지 않게 취득이 가능한 수준으로 판단됩니다.
2022년 6월부터 시험환경이 바뀌었습니다.
PSI 에서 제공되는 시큐어 브라우저를 통해서 제공되는 환경에서 시험을 보게 됩니다.
6월에 비해 많이 개선됬다고는 하나 시험보는데 상당히 불편한 점이 여러가지 있었습니다.
(속도라던가... 복붙이라던가..북마크 사용 불가라던가 등등등)
제가 못찾은 건지 모르겠으나, 노트패드를 못찾아서 vim을 하나 더 띄워서 노트패드로 사용하였습니다.(tmux사용 가능함)
공부 순서는 하기와 같습니다.
1. 인프런 데브옵스(DevOps)를 위한 쿠버네티스 마스터
도커 및 쿠버네티스에 대한 전반적인 개념을 잡기 좋은 강의라고 생각 됩니다.
자격증 취득보단 실제 쿠버네티스의 각 기능별 이해도를 높이기 좋습니다. 전 쿠버네티스에 대한 전반적인 지식을 쌓기 위해 수강하였습니다.
수강료가 꽤 비싼 편이어서, 꼭 이 강의를 듣는다기 보다는 전반적인 쿠버네티스를 이해할 수 있는 강의 혹은 책을 보시면 될 것 같습니다.
데브옵스(DevOps)를 위한 쿠버네티스 마스터 - 인프런 | 강의
컨테이너 기반 오픈 소스 가상화 프로젝트인 "쿠버네티스"를 이용한 컨테이너 환경의 분산 시스템을 탄력적으로 실행하기 위한 프레임 워크를 활용하는 방법을 입문부터 활용까지 다룹니다., -
www.inflearn.com
2. Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA) with Practice Tests
CKA 자격증 취득관련해서 검색하면 나오는 가장 유명한 뭄샤드의 Udemy강의 입니다.
강의는 할인을 자주하며 약 1~2만원대로 구매가 가능하니 할인 할때 구매 하시면 됩니다.
1번에서 이야기한 전체적인 이론에 대한 부분이 전체적인 수강의 대부분을 차지하고 있으며,
실제 시험을 위한 부분은 Mock Exam 부분이라고 생각됩니다.
영어에 어려움이 없으시면 이 강의만 들어도 크게 무리는 없을 것으로 예상되며,
Mock Exam은 익숙해질때까지 꼭 풀어보시길 권장 드립니다.
강의는 지속적으로 업데이트 되는 것으로 알고 있습니다.
https://www.udemy.com/course/certified-kubernetes-administrator-with-practice-tests/
3. 따베런(따배씨 CKA시리즈)
CKA 준비하면서 알게된 유투브 입니다.
현재는 유료화 컨텐츠로 전환되어서 4편 이후로는 별도의 비용이 발생합니다. (1만원 미만)
CKA 취득관련하여 시험문제에 대한 30가지 유형별로 설명 및 풀이영상이며, 시험전에 최종적으로 보시면 좋을 걸로 생각됩니다.
실제로 제가 푼 Mock Exam 에 없는 유형도 있어서 도움을 받았습니다.
시간이 된다면 가급적이면 쿠버네티스 강의시리즈(기본, 심화)도 보시면 좋습니다.

현재 실 업무에서 직접 담당하는 상태는 아니기 때문에 CKAD취득까지는 바로 이어지지 않을 것 같습니다.
다만 시험 자체가 실습 형태로 이우어지다보니 쿠버네티스를 이해하는데 도움이 많이 되는 시험이라고 생각되어, 관련 업무를 하실 경우 취득하시기를 권장 드립니다.
[우아하게 앤서블] Chapter 6 - 플레이북을 효율적으로 작성하기
플레이북의 동적인 사용을 테스트 하기 위해
CentOS * 5, Ubuntu * 5 환경으로 구성
Vagrantfile
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
#==============#
# CentOS nodes #
#==============#
#Ansible-Node101
config.vm.define "ansible-node101" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Node101(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node101"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.101"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60101, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "bash_ssh_conf_4_CentOS.sh"
end
#Ansible-Node102
config.vm.define "ansible-node102" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Node102(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node102"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.102"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60102, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "bash_ssh_conf_4_CentOS.sh"
end
#Ansible-Node103
config.vm.define "ansible-node103" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Node103(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node103"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.103"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60103, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "bash_ssh_conf_4_CentOS.sh"
end
#Ansible-Node104
config.vm.define "ansible-node104" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Node104(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node104"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.104"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60104, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "bash_ssh_conf_4_CentOS.sh"
end
#Ansible-Node105
config.vm.define "ansible-node105" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Node105(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node105"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.105"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60105, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "bash_ssh_conf_4_CentOS.sh"
end
#==============#
# Ubuntu nodes #
#==============#
#Ansible-Node201
config.vm.define "ansible-node201" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Node201(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node201"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.201"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60201, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
end
#Ansible-Node202
config.vm.define "ansible-node202" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Node202(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node202"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.202"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60202, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
end
#Ansible-Node203
config.vm.define "ansible-node203" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Node203(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node203"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.203"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60203, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
end
#Ansible-Node204
config.vm.define "ansible-node204" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Node204(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node204"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.204"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60204, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
end
#Ansible-Node205
config.vm.define "ansible-node205" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Node205(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node205"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.205"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60205, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
end
#================#
# Ansible Server #
#================#
config.vm.define "ansible-server" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Server(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-server"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.10"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60010, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "yum install epel-release -y"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "yum install ansible -y"
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ansible_env_ready.yml",
destination: "ansible_env_ready.yml"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "ansible-playbook ansible_env_ready.yml"
end
end앤서블 환경 구성 파일
ansible_env_ready.yml
---
- name: Setup for the Ansible's Environment
hosts: localhost
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: Add "/etc/ansible/hosts"
blockinfile:
path: /etc/ansible/hosts
block: |
[nodes]
192.168.0.[101:105]
192.168.0.[201:205]
- name: Generate sshkey
become: yes
become_user: vagrant
shell: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "ssh-keyscan 192.168.0.101 >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts"
- "ssh-keyscan 192.168.0.102 >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts"
- "ssh-keyscan 192.168.0.103 >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts"
- "ssh-keyscan 192.168.0.104 >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts"
- "ssh-keyscan 192.168.0.105 >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts"
- "ssh-keyscan 192.168.0.201 >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts"
- "ssh-keyscan 192.168.0.202 >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts"
- "ssh-keyscan 192.168.0.203 >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts"
- "ssh-keyscan 192.168.0.204 >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts"
- "ssh-keyscan 192.168.0.205 >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts"
- name: Create vim env's directories & files
shell: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "mkdir -p /home/vagrant/.vim/autoload /home/vagrant/.vim/bundle"
- "touch /home/vagrant/.vimrc"
- "touch /home/vagrant/.bashrc"
- name: Install vim-enhanced
yum:
name: vim-enhanced
state: present
- name: Install git
yum:
name: git
state: present
- name: Download pathogen.vim
shell: "curl -fLo /home/vagrant/.vim/autoload/pathogen.vim
https://tpo.pe/pathogen.vim"
- name: Git clone vim-ansible-yaml
git:
repo: https://github.com/chase/vim-ansible-yaml.git
dest: /home/vagrant/.vim/bundle/vim-ansible-yaml
- name: Configure vimrc
lineinfile:
path: /home/vagrant/.vimrc
line: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "set number"
- "execute pathogen#infect()"
- "syntax on"
- name: Configure Bashrc
lineinfile:
path: /home/vagrant/.bashrc
line: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "alias ans='ansible'"
- "alias anp='ansible-playbook'"기존 노드 모두 삭제 진행
vagrant up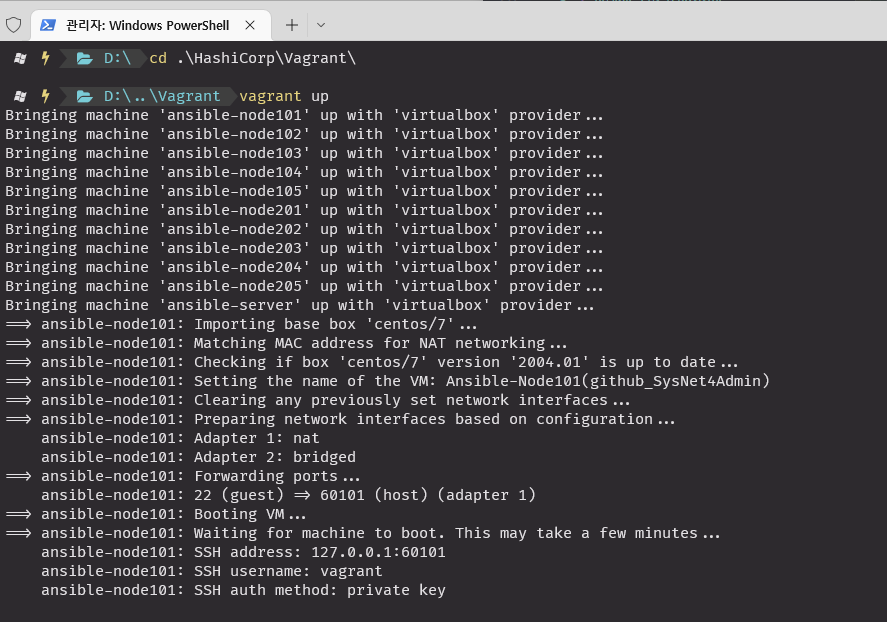
핑체크
vagrant ssh ansible-server
ans nodes -m ping -k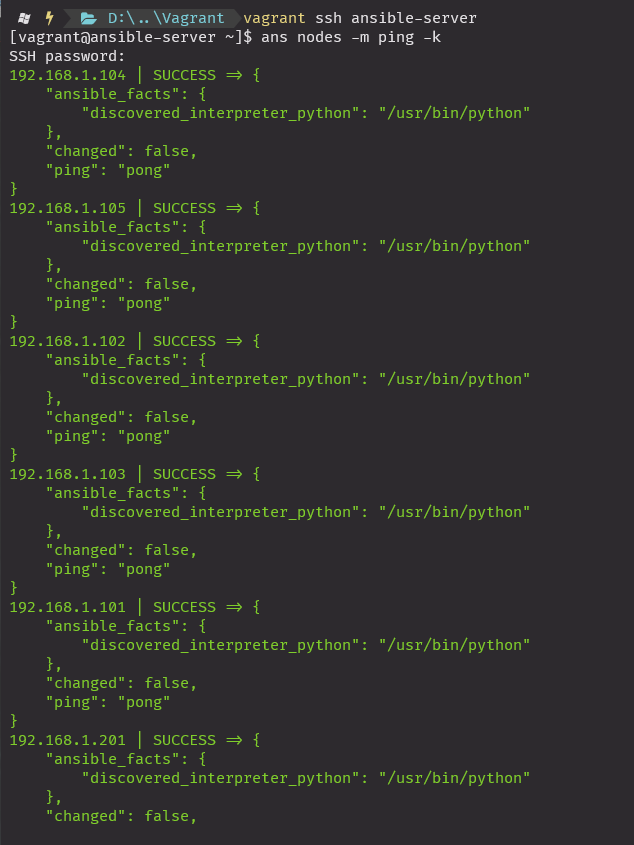
known_hosts를 자동으로 등록하기
Vagrantfile
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
#==============#
# CentOS nodes #
#==============#
#Ansible-Node101
config.vm.define "ansible-node101" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Node101(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node101"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.101"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60101, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "bash_ssh_conf_4_CentOS.sh"
end
#Ansible-Node102
config.vm.define "ansible-node102" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Node102(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node102"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.102"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60102, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "bash_ssh_conf_4_CentOS.sh"
end
#Ansible-Node103
config.vm.define "ansible-node103" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Node103(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node103"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.103"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60103, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "bash_ssh_conf_4_CentOS.sh"
end
#Ansible-Node104
config.vm.define "ansible-node104" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Node104(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node104"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.104"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60104, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "bash_ssh_conf_4_CentOS.sh"
end
#Ansible-Node105
config.vm.define "ansible-node105" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Node105(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node105"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.105"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60105, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "bash_ssh_conf_4_CentOS.sh"
end
#==============#
# Ubuntu nodes #
#==============#
#Ansible-Node201
config.vm.define "ansible-node201" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Node201(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node201"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.201"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60201, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
end
#Ansible-Node202
config.vm.define "ansible-node202" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Node202(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node202"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.202"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60202, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
end
#Ansible-Node203
config.vm.define "ansible-node203" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Node203(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node203"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.203"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60203, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
end
#Ansible-Node204
config.vm.define "ansible-node204" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Node204(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node204"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.204"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60204, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
end
#Ansible-Node205
config.vm.define "ansible-node205" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Node205(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node205"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.205"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60205, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
end
#================#
# Ansible Server #
#================#
config.vm.define "ansible-server" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Server(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-server"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.10"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60010, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "yum install epel-release -y"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "yum install ansible -y"
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ansible_env_ready.yml",
destination: "ansible_env_ready.yml"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "ansible-playbook ansible_env_ready.yml"
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "auto_pass.yml", destination: "auto_pass.yml"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "ansible-playbook auto_pass.yml", privileged: false
end
endansible_env_ready.yml
---
- name: Setup for the Ansible's Environment
hosts: localhost
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: Add "/etc/ansible/hosts"
blockinfile:
path: /etc/ansible/hosts
block: |
[nodes]
192.168.0.[101:105]
192.168.0.[201:205]
- name: Create vim env's directories & files
shell: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "mkdir -p /home/vagrant/.vim/autoload /home/vagrant/.vim/bundle"
- "touch /home/vagrant/.vimrc"
- "touch /home/vagrant/.bashrc"
- name: Install vim-enhanced
yum:
name: vim-enhanced
state: present
- name: Install git
yum:
name: git
state: present
- name: Download pathogen.vim
shell: "curl -fLo /home/vagrant/.vim/autoload/pathogen.vim
https://tpo.pe/pathogen.vim"
- name: Git clone vim-ansible-yaml
git:
repo: https://github.com/chase/vim-ansible-yaml.git
dest: /home/vagrant/.vim/bundle/vim-ansible-yaml
- name: Configure vimrc
lineinfile:
path: /home/vagrant/.vimrc
line: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "set number"
- "execute pathogen#infect()"
- "syntax on"
- name: Configure Bashrc
lineinfile:
path: /home/vagrant/.bashrc
line: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "alias ans='ansible'"
- "alias anp='ansible-playbook'"auto_pass.yml
---
- name: Create authority between server and nodes
hosts: nodes
connection: local
serial: 1
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: ssh-keyscan for known_hosts file
command: /usr/bin/ssh-keyscan -t ecdsa {{ ansible_host }}
register: keyscan
- name: input key
lineinfile:
path: ~/.ssh/known_hosts
line: "{{ item }}"
create: yes
with_items:
- "{{ keyscan.stdout_lines }}"삭제 후 재생성
vag_reconf.bat재 생성 후
vagrant ssh ansible-server
ans nodes -m ping -k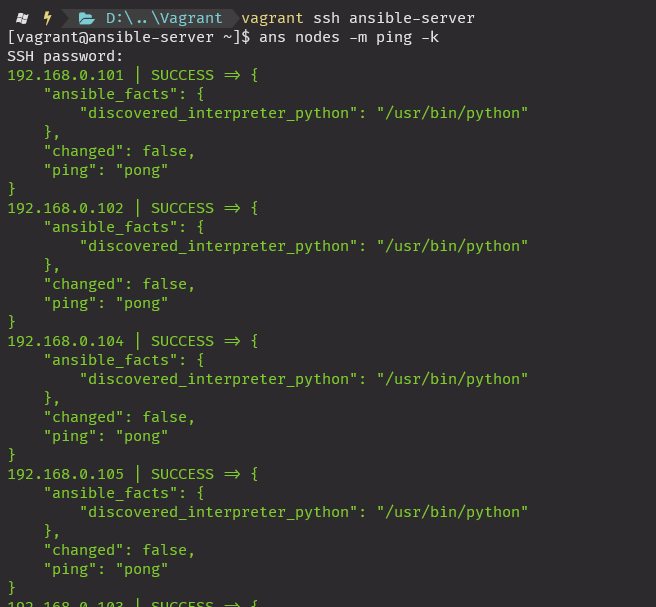
authorizeD_keys 등록
auto_pass.yml
---
- name: Create authority between server and nodes
hosts: nodes
connection: local
serial: 1
gather_facts: no
vars:
ansible_password: vagrant
tasks:
- name: ssh-keyscan for known_hosts file
command: /usr/bin/ssh-keyscan -t ecdsa {{ ansible_host }}
register: keyscan
- name: input key
lineinfile:
path: ~/.ssh/known_hosts
line: "{{ item }}"
create: yes
with_items:
- "{{ keyscan.stdout_lines }}"
- name: sshkeygen for authorized_keys file
command: "ssh-keygen -b 2048 -t rsa -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa -q -N ''"
ignore_errors: yes
run_once: true
- name: input key for each node
connection: ssh
authorized_key:
user: vagrant
state: present
key: "{{ lookup('file', '~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub') }}"변경 후 ansible 서버 프로비져닝
vagrant provision ansible-server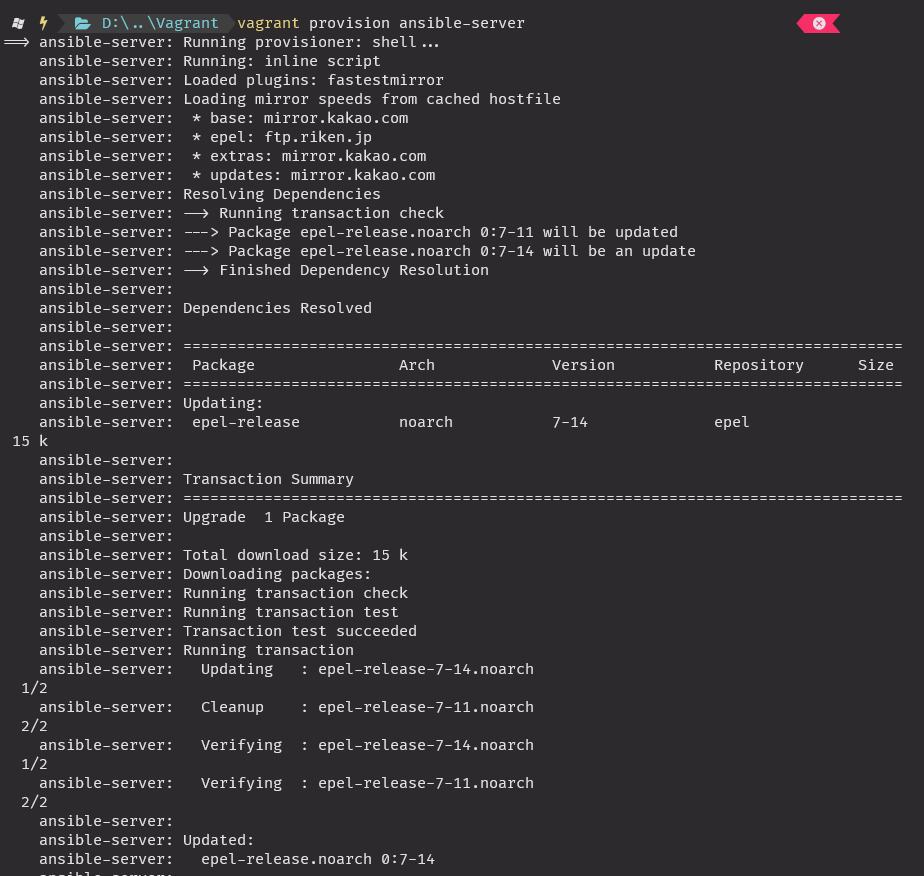
암호 없이 핑체크
vagrant ssh ansible-server
ans -m ping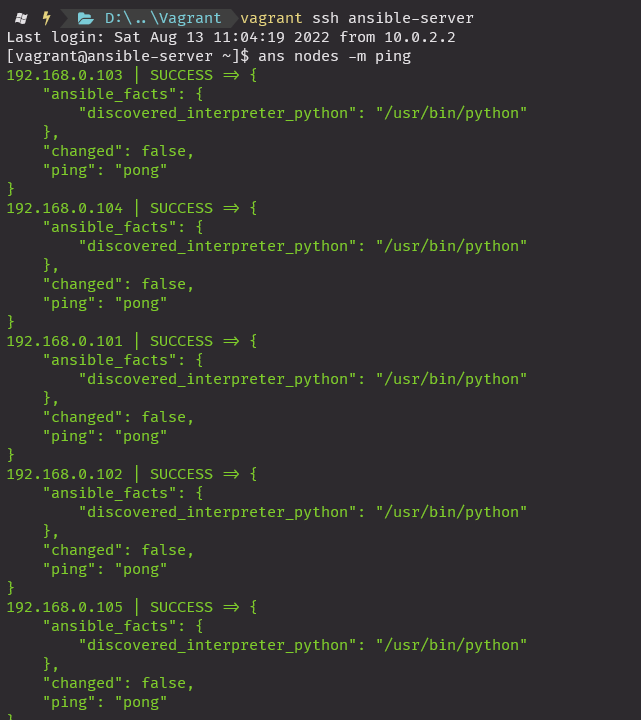
플레이북 동적으로 구성하기
gather_facts: no
-> facts를 수집하지 않음. 앤서블 노드들의 다양한 정보를 미리 정의해둔 변수
facts.yml
---
- name: print ipv4.address for nodes
hosts: nodes
#gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: debug by msg
debug:
msg:
- "eth0's ip {{ ansible_eth0.ipv4.address }}"
- "eth1's ip {{ ansible_eth1.ipv4.address }}"
- name: debug by var
debug:
var: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- hostvars[inventory_hostname]['ansible_eth0']['ipv4']['address']
- hostvars[inventory_hostname]['ansible_eth1']['ipv4']['address']anp facts.yml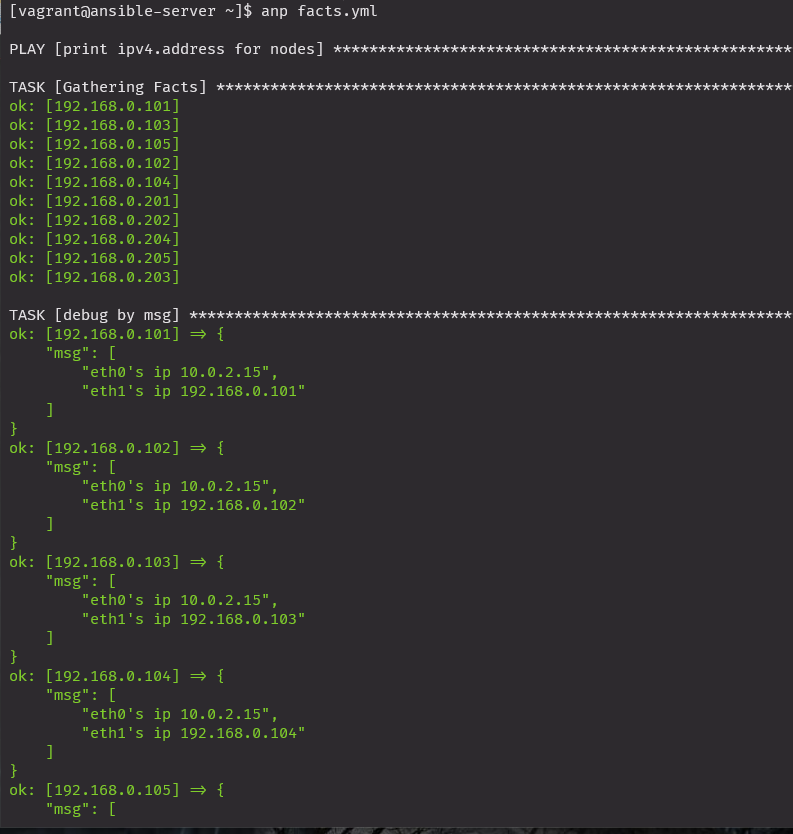
facts확인
ans nodes -m setup > facts.txt
추출한 정보로 특정정보 확인
cat facts.txt | grep SSH_CONNECTION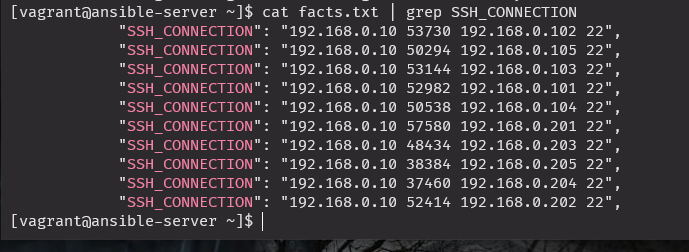
각 노드별로 출력해주는 --tree명령어
--tree명령을 토앻서 저장된 facts 한줄로 표기(JSON형태)
ans nodes -m setup --tree /tmp/facts > /dev/null
ls /tmp/fats
cat /tmp/facts/192.168.0.101
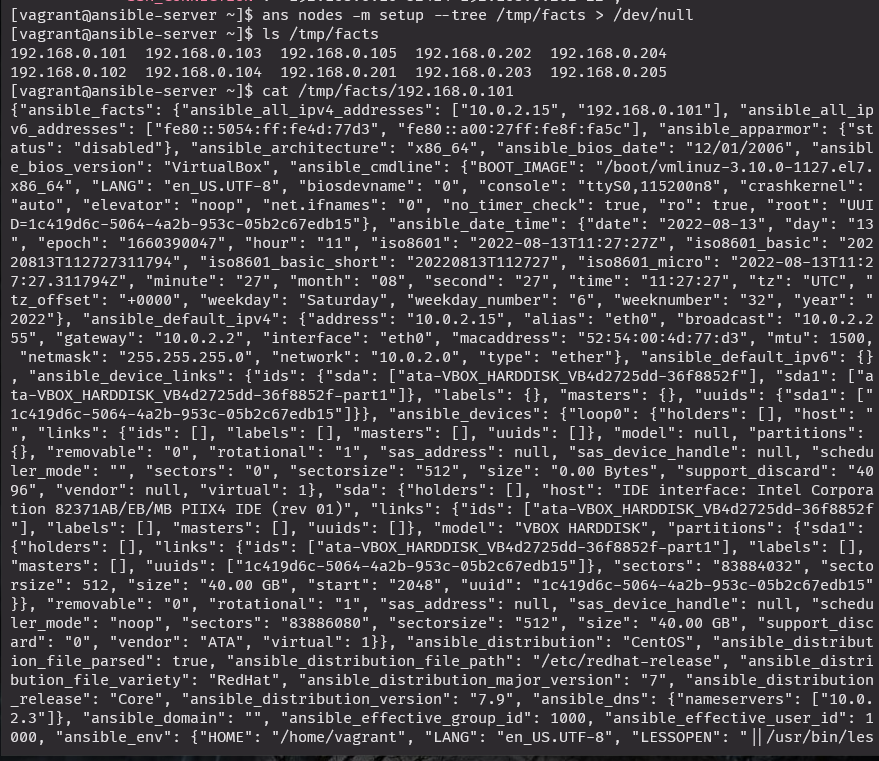
facts_collector.yml
---
- name: Collect facts for each node
hosts: nodes
tasks:
- name: generate facts
setup:
register: facts
- name: save facts
local_action:
module: copy
content: "{{ facts | to_nice_json }}"
dest: ./{{ ansible_hostname }}_facts_by_collector.txtanp facts_collector.yml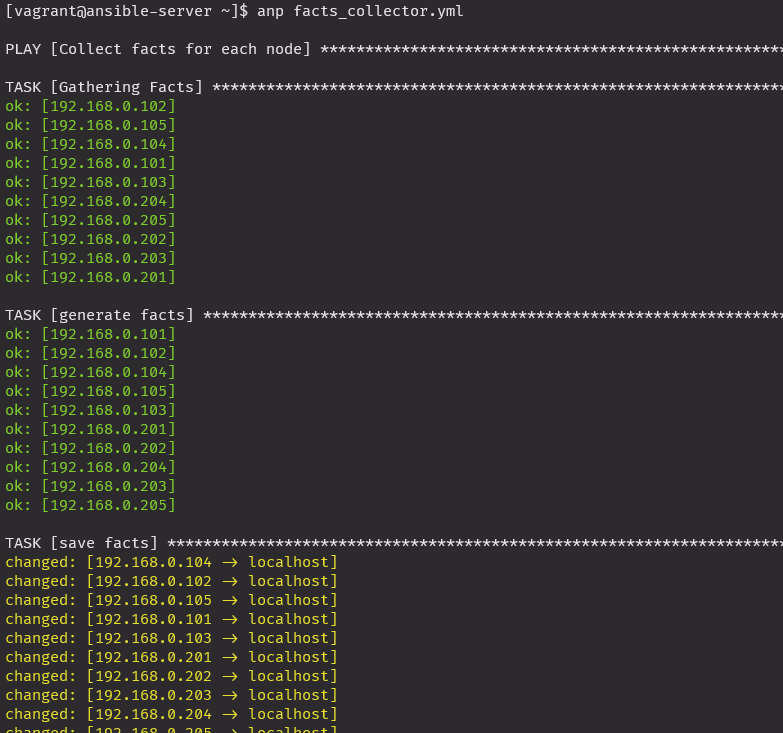
ls -lh ansible*
파일 확인
cat ansible-node101_facts_by_collector.txt | grep SSH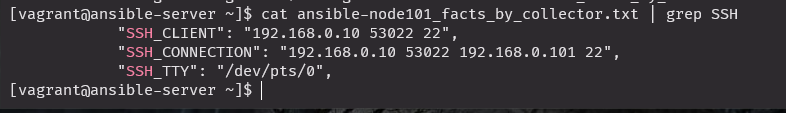
when 조건
nginx_install_w_when.yml
우분투에서 nginx 사이트 오류 발생해서 apache.com으로 변경
---
- name: Install nginx on the nodes
hosts: nodes
become: yes
tasks:
- name: install epel-release for CentOS
action: "{{ ansible_pkg_mgr }} name=epel-release state=latest"
when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS'
- name: install nginx web server for CentOS
action: "{{ ansible_pkg_mgr }} name=nginx state=present"
when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS'
- name: upload default index.html for web server
get_url: url=https://www.nginx.com dest=/usr/share/nginx/html/ mode=0644
when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS'
- name: start nginx web server
service: name=nginx state=started
when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS'
- name: install nginx web server for Ubuntu
action: "{{ ansible_pkg_mgr }} name=nginx state=present update_cache=yes"
when: ansible_distribution == 'Ubuntu'
- name: upload default index.html for web server
get_url: url=https://www.apache.com dest=/usr/share/nginx/html/
mode=0644 validate_certs=no
when: ansible_distribution == 'Ubuntu'nginx_remove_w_when.yml
---
- name: Remove nginx on the nodes
hosts: nodes
become: yes
tasks:
- name: remove epel-release for CentOS
action: "{{ ansible_pkg_mgr }} name=epel-release state=absent"
when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS'
- name: remove nginx web server for CentOS
action: "{{ ansible_pkg_mgr }} name=nginx state=absent"
when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS'
- name: remove nginx web server
action: "{{ ansible_pkg_mgr }} name=nginx state=absent autoremove=yes"
when: ansible_distribution == 'Ubuntu'설치 실행 (OS 체크해서 진행)
anp nginx_install_w_when.yml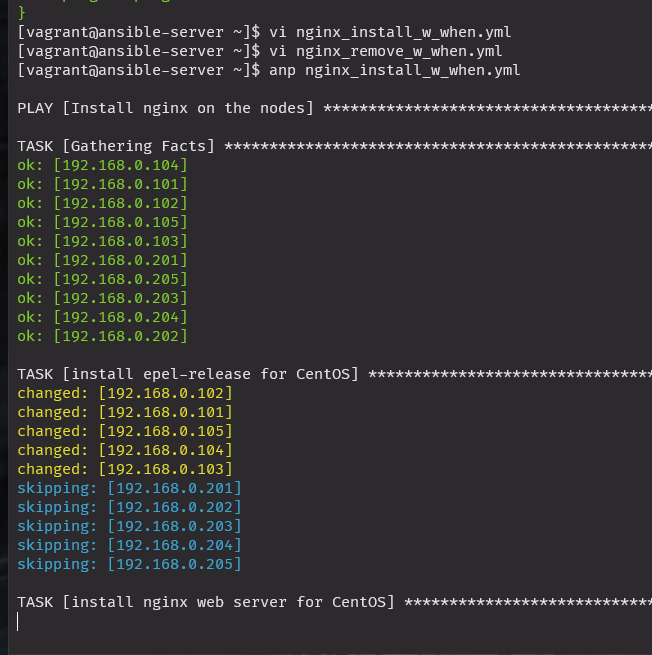
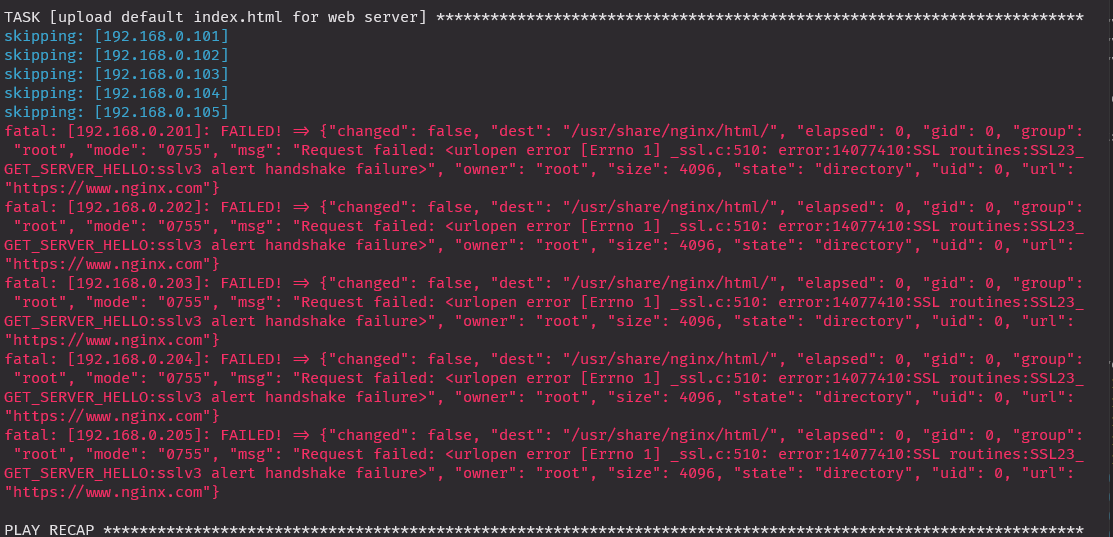
nginx 삭제 진행
anp nginx_remove_w_when.yml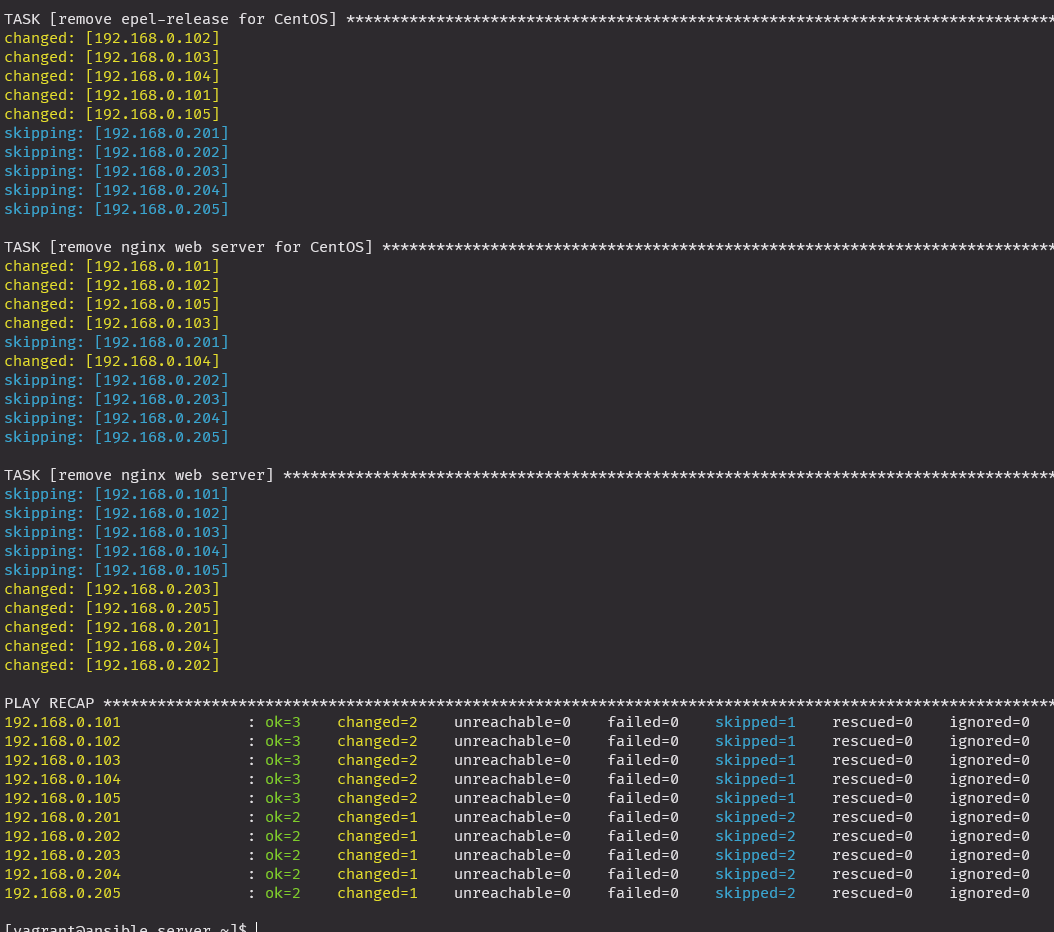
include_tasks
낭비를 줄이기 위한 코드 개선
nginx_install_w_include_tasks.yml
---
- name: Install nginx on the nodes
hosts: nodes
become: yes
tasks:
- name: nginx for CentOS
include_tasks: CentOS.yml
when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS'
- name: nginx for Ubuntu
include_tasks: Ubuntu.yml
when: ansible_distribution == 'Ubuntu'CentOS.yml
- name: install epel-release
action: "{{ ansible_pkg_mgr }} name=epel-release state=latest"
- name: install nginx web server
action: "{{ ansible_pkg_mgr }} name=nginx state=present"
- name: upload default index.html for web server
get_url: url=https://www.nginx.com dest=/usr/share/nginx/html/ mode=0644
- name: start nginx web server
service: name=nginx state=startedUbuntu.yml
- name: install nginx web server
action: "{{ ansible_pkg_mgr }} name=nginx state=present update_cache=yes"
- name: upload default index.html for web server
get_url: url=https://www.apache.com dest=/usr/share/nginx/html/
mode=0644 validate_certs=nonginx_remove_w_include_tasks.yml
---
- name: Remove nginx on the nodes
hosts: nodes
become: yes
tasks:
- name: nginx for CentOS
include_tasks: CentOS_remo.yml
when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS'
- name: nginx for Ubuntu
include_tasks: Ubuntu_remo.yml
when: ansible_distribution == 'Ubuntu'CentOS_remo.yml
- name: remove epel-release
action: "{{ ansible_pkg_mgr }} name=epel-release state=absent"
- name: remove nginx web server
action: "{{ ansible_pkg_mgr }} name=nginx state=absent"Ubuntu_remo.yml
- name: remove nginx web server
action: "{{ ansible_pkg_mgr }} name=nginx state=absent autoremove=yes"
실행
anp nginx_install_w_include_tasks.yml
설치확인

삭제
anp nginx_remove_w_include_task.yml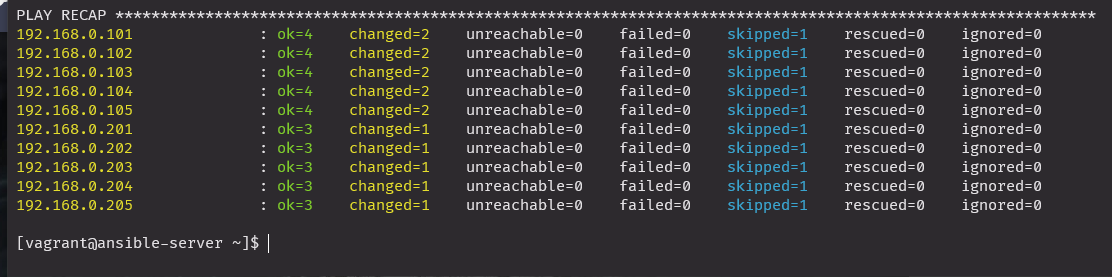
if 구문 활용
nginx_install_w_if.yml
---
- name: Install nginx on the nodes
hosts: nodes
become: yes
vars:
lnx_name: "{{ 'CentOS' if ansible_distribution == 'CentOS'
else 'Ubuntu' if ansible_distribution == 'Ubuntu'
else 'Just Linux' }}"
tasks:
- name: nginx for any linux
include_tasks: "{{ lnx_name }}.yml"anp nginx_instal_w_if.yml
nginx_remove_w_if.yml
---
- name: Remove nginx on the nodes
hosts: nodes
become: yes
vars:
lnx_name: "{{ 'CentOS' if ansible_distribution == 'CentOS'
else 'Ubuntu' if ansible_distribution == 'Ubuntu'
else 'Just Linux' }}"
tasks:
- name: nginx for any linux
include_tasks: "{{ lnx_name }}_remo.yml"anp nginx_remove_w_if.yml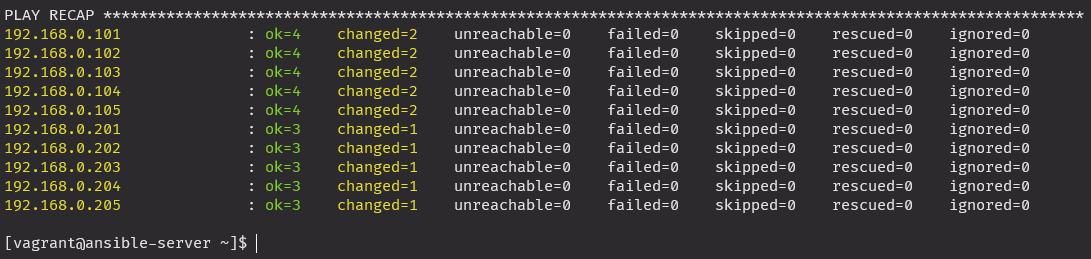
NFS 구성을 효율적으로 하기
nfs_adv.yml
---
- name: Setup for nfs server
hosts: localhost
tasks:
- include_tasks: nfs_server.yml
- name: Setup for nfs clients
hosts: nodes
tasks:
- include_tasks: nfs_clients.ymlnfs_server.yml
- name: make nfs_shared directory
file:
path: "{{ ansible_user_dir }}/nfs_shared"
state: directory
mode: 0777
- name: configure /etc/exports
become: yes
lineinfile:
path: /etc/exports
line: "{{ ansible_user_dir }}/nfs_shared 192.168.0.0/24(rw,sync)"
- name: nfs service restart
become: yes
service:
name: nfs
state: restartednfs_client.yml
- name: make nfs_client directory
file:
path: "{{ ansible_user_dir }}/nfs"
state: directory
- name: mount point directory as client
become: yes
mount:
name: "{{ ansible_user_dir }}/nfs"
src: "{{ ansible_env.SSH_CLIENT.split()[0] }}:/home/vagrant/nfs_shared"
fstype: nfs
opts: nfsvers=3
state: mounted실행
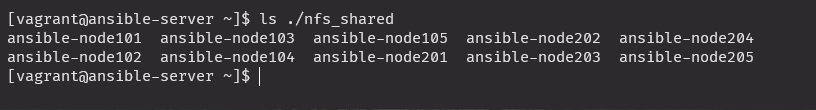
anp nfs_adv.uml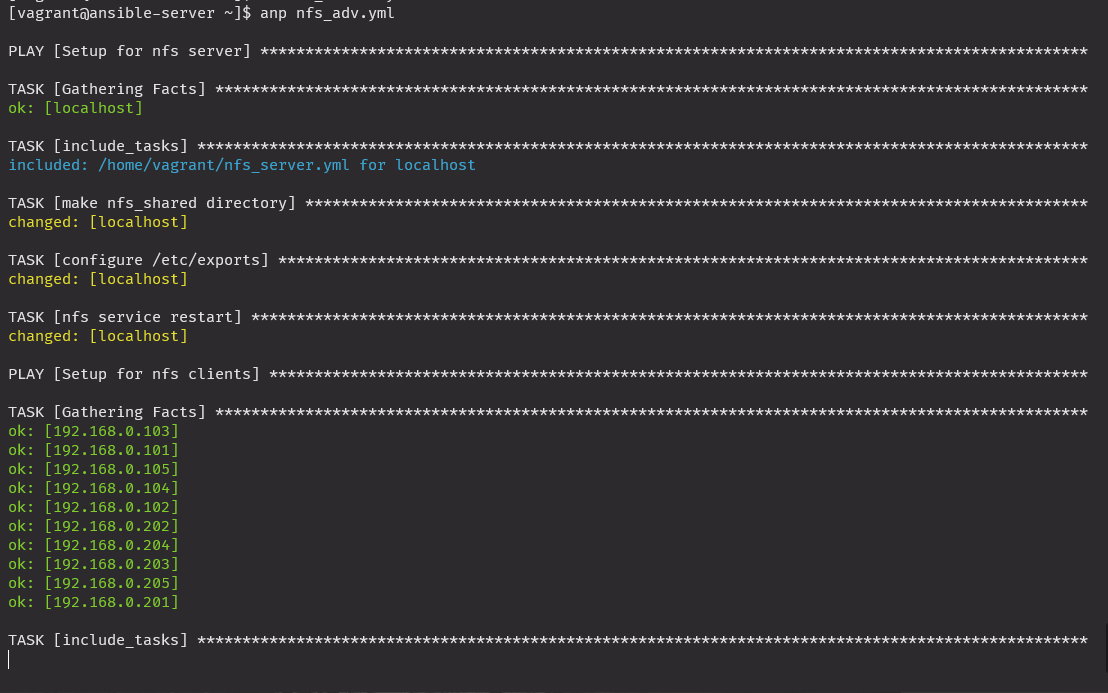
ans nodes -m shell -a "cat /etc/hostname | xargs -i touch ./nfs/{}"
ls ./nfs_shared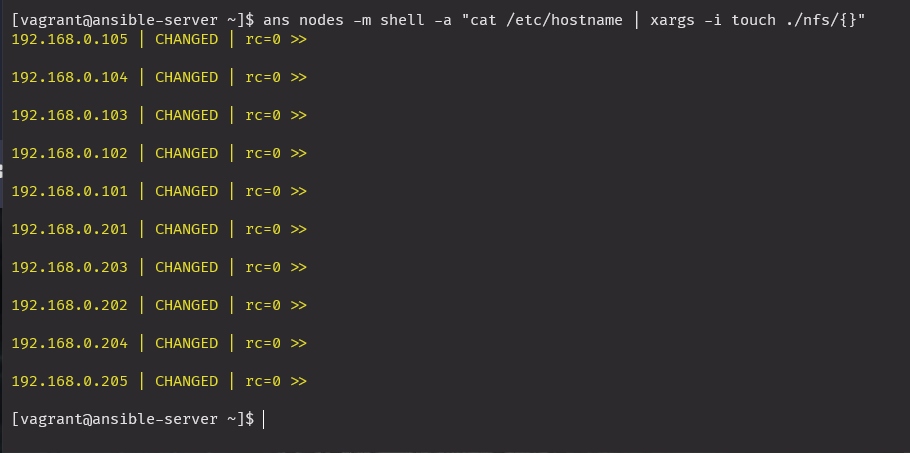
넥서스 스위치의 구성 파일을 효율적으로 백업하기 -> 장비 없어서 패스
Cumulus로 접속하기 위한 인증을 자동화 하기
Vagrantfile
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
#===============#
# Cumulus nodes #
#===============#
#Ansible-Cumulus01
config.vm.define "ansible-cl01" do |cl|
cl.vm.box = "CumulusCommunity/cumulus-vx"
cl.vm.box_version = "3.6.0"
cl.vm.box_check_update = false
cl.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Cumulus01(github_SysNet4Admin)"
vb.customize ['modifyvm', :id, '--macaddress1', '080027000061']
vb.customize ['modifyvm', :id, '--natnet1', '10.0.61.0/24']
end
cl.vm.host_name = "ansible-cl01"
cl.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.61"
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp2", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp3", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp4", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60061, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cl.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
end
#Ansible-Cumulus02
config.vm.define "ansible-cl02" do |cl|
cl.vm.box = "CumulusCommunity/cumulus-vx"
cl.vm.box_version = "3.6.0"
cl.vm.box_check_update = false
cl.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Cumulus02(github_SysNet4Admin)"
vb.customize ['modifyvm', :id, '--macaddress1', '080027000062']
vb.customize ['modifyvm', :id, '--natnet1', '10.0.62.0/24']
end
cl.vm.host_name = "ansible-cl02"
cl.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.62"
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp2", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp3", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp4", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60062, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cl.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
end
#Ansible-Cumulus03
config.vm.define "ansible-cl03" do |cl|
cl.vm.box = "CumulusCommunity/cumulus-vx"
cl.vm.box_version = "3.6.0"
cl.vm.box_check_update = false
cl.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Cumulus03(github_SysNet4Admin)"
vb.customize ['modifyvm', :id, '--macaddress1', '080027000063']
vb.customize ['modifyvm', :id, '--natnet1', '10.0.63.0/24']
end
cl.vm.host_name = "ansible-cl03"
cl.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.63"
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp2", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp3", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp4", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60063, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cl.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
end
#Ansible-Cumulus04
config.vm.define "ansible-cl04" do |cl|
cl.vm.box = "CumulusCommunity/cumulus-vx"
cl.vm.box_version = "3.6.0"
cl.vm.box_check_update = false
cl.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Cumulus04(github_SysNet4Admin)"
vb.customize ['modifyvm', :id, '--macaddress1', '080027000064']
vb.customize ['modifyvm', :id, '--natnet1', '10.0.64.0/24']
end
cl.vm.host_name = "ansible-cl04"
cl.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.64"
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp2", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp3", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp4", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60064, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cl.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
end
#================#
# Ansible Server #
#================#
config.vm.define "ansible-server" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Server(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-server"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.10"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60010, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "yum install epel-release -y"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "yum install ansible -y"
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ansible_env_ready.yml",
destination: "ansible_env_ready.yml"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "ansible-playbook ansible_env_ready.yml"
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "cl_auto_pass.yml", destination: "cl_auto_pass.yml"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "ansible-playbook cl_auto_pass.yml",
privileged: false
end
endansible_env_ready.yml
---
- name: Setup for the Ansible's Environment
hosts: localhost
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: Add "/etc/ansible/hosts"
blockinfile:
path: /etc/ansible/hosts
block: |
[spine]
192.168.0.61
192.168.0.62
[leaf]
192.168.0.63
192.168.0.64
[cl:children]
spine
leaf
- name: Create vim env's directories & files
shell: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "mkdir -p /home/vagrant/.vim/autoload /home/vagrant/.vim/bundle"
- "touch /home/vagrant/.vimrc"
- "touch /home/vagrant/.bashrc"
- name: Install vim-enhanced
yum:
name: vim-enhanced
state: present
- name: Install git
yum:
name: git
state: present
- name: Download pathogen.vim
shell: "curl -fLo /home/vagrant/.vim/autoload/pathogen.vim
https://tpo.pe/pathogen.vim"
- name: Git clone vim-ansible-yaml
git:
repo: https://github.com/chase/vim-ansible-yaml.git
dest: /home/vagrant/.vim/bundle/vim-ansible-yaml
- name: Configure vimrc
lineinfile:
path: /home/vagrant/.vimrc
line: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "set number"
- "execute pathogen#infect()"
- "syntax on"
- name: Configure Bashrc
lineinfile:
path: /home/vagrant/.bashrc
line: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "alias ans='ansible'"
- "alias anp='ansible-playbook'"cl_auto_pass.yml
---
- name: Create authority between ansible-server and cumulus-nodes
hosts: cl
connection: local
vars:
ansible_password: vagrant
ansible_become_pass: CumulusLinux!
tasks:
- name: ssh-keyscan for known_hosts file
command: /usr/bin/ssh-keyscan -t ecdsa {{ ansible_host }}
register: keyscan
- name: input key
lineinfile:
path: ~/.ssh/known_hosts
line: "{{ item }}"
create: yes
with_items:
- "{{ keyscan.stdout_lines }}"
- name: ssh-keygen for authorized_keys file
command: |
ssh-keygen -C cumulus@{{ ansible_hostname }} \
-b 2048 -t rsa -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa -q -N ''
ignore_errors: yes
run_once: true
- name: input key for each node
connection: ssh
become: yes
authorized_key:
user: cumulus
state: present
key: "{{ lookup('file', '~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub') }}"vm 전체 삭제 후 재생성
vagrant up인증 확인
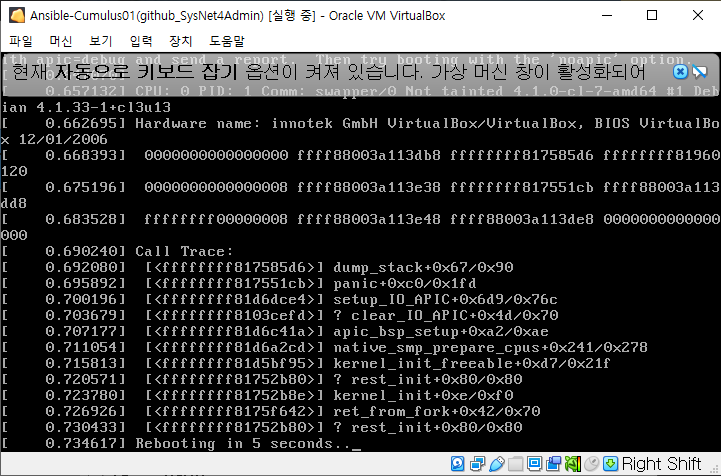
cumulus에 대한 인증 추가이므로 유저를 추가해주어야 함
anp cl -m ping
anp cl -m ping --user cumulus무한재부팅....증상으로 우선 마무리..ㅠㅠ
AWS (CP, SAA, SAP), 리눅스 마스터2급
Redplug입니다.
Azure 쪽은 필요한(?) 자격증은 따놓은 상태였고
Azure만 하는것보단 AWS쪽도 같이 할수 있으면 좋지 않을까 해서 솔루션 아키텍트쪽으로 따기 시작했습니다.
SAP까지 따놓은 상태긴 하나 덤프 위주로 공부를 한터라 사실 AWS를 잘안다고는 보기 어렵지 않을까 싶습니다.
이제 하나만 더 따면 올해 생각했던 자격증은 모두 취득을 하는 상황이라
남은기간 동안 또 열심히 해봐야겠네요.
AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner
준비하면서 크게 어려움은 없었던것 같네요.
Azure쪽 기본 자격증은 유효기간이 없는데 AWS는 기본 자격증도 유효기간이 있네요

AWS Certified Solutions Architect -Associate
기술적인 내용이 많아 나와서 덤프를 풀면서 해당 솔루션들에 대해서 찾아보면서 도움이 많이 되었던것 같습니다.(대부분 덤프에서 나옴)

AWS Certified Solutions Architect - Professional
기술적인 측면보다는 특정 시나리오에서 요구되는 목적에 대해서 방법을 찾는 질문들이 많아서 실제 SA업무를 하게 될 경우에 발생할 수 있는 고민들을 문제로 주어지지 않았나 생각됩니다. 물론 현실은 더욱더 복잡한 상황에 놓일 경우가 많긴 하겠지만요. 정신이 없던 시기였던터라 가지고 있던 덤프도 끝까지 보질 못했는데 다행히 턱걸이로 붙었서 다행이었다고 생각합니다.
https://www.examtopics.com/ 의 덤프를 활용하였고, 70-80% 정도 나온것 같고 보지못했던 생소한 문제들도 좀 있었던걸로 기억합니다.
https://oacle.net/home 여러사이트 덤프를 섞어서 문제풀이 형식으로 풀수 있는 사이트 입니다.

리눅스마스터 2급
시험보기전에 찾아봤던 내용도 그렇고 막상 시험을 보고나서도 느끼긴 했지만...
뭔가 실무와 동떨어진 느낌이 어느정도 있지 않나 싶습니다.
향후에 LPIC쪽으로 자격증을 취득하고 싶다라는 생각은 가지고 있는 상태입니다.
1차 시험은 온라인 오픈북 시험이라 검색하면서 볼수 있습니다.(...도대체 왜보는건지..)
2차 시험은 오프라인으로 보게되며, 시험 자체는 문제은행에서 출제되는 방식이기 때문에 기존 기출문제를 꼼꼼히 보게되면 크게 무리 없이 합격할 걸로 보입니다.기출문제는 시험사이트를 찾아가시거나 모아둔 사이트들을 찾으면 많이 나옵니다.전 한3 년치 정도를 보고 시험보았습니다.

[우아하게 앤서블] Chapter 5 - 네트워크 운영체제를 앤서블을 통해서 관리하기
4장까지는 Hyper-V 환경에서 구성을 진행하였으나 Vagrant 자체에서 Hyper-V용 Box를 지원하지 않는 부분이 발견되면서 결국은 VirtualBOX로 전환하였습니다. 5장의 실습 OS인 VyOS도 지원하지 않음 ㅠㅠ
VyOS로 검색 시 HyperV한건 나오나 다운로드 수가 많지 않아서 리스크를 가지고 실습하기엔 사실 귀찮은 면이 있어서..

결국 설치 진행...
공부를 하면서 다른 환경에서 구성을 맞춰가는게 나름 재미있는 요소중 하나였는데 좀 아쉽네요.
환경은 데탑에서 원래 Hyper-V를 활용중이었던 터라 날릴수가 없어서 노트북 환경으로 변경 진행
장 초반인 NX-OS는 물리장비로 진행하는 부분이 어서 패스
VyOS설치를 위한 셋팅
Vagrantfile
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
#============#
# VyOS Nodes #
#============#
#Ansible-VyOS01
config.vm.define "ansible-vyos01" do |vy|
vy.vm.box = "sysnet4admin/VyOS"
vy.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-VyOS01(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
vy.vm.host_name = "ansible-vyos01"
vy.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.1.51"
vy.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60051, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
vy.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "eth2", auto_config: false
vy.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "eth3", auto_config: false
vy.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
vy.vbguest.auto_update = false
end
#Ansible-VyOS02
config.vm.define "ansible-vyos02" do |vy|
vy.vm.box = "sysnet4admin/VyOS"
vy.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-VyOS02(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
vy.vm.host_name = "ansible-vyos02"
vy.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.1.52"
vy.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60052, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
vy.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "eth2", auto_config: false
vy.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "eth3", auto_config: false
vy.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
vy.vbguest.auto_update = false
end
#================#
# Ansible Server #
#================#
config.vm.define "ansible-server" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Server(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-server"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.1.10"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60010, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "yum install epel-release -y"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "yum install ansible -y"
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ansible_env_ready.yml",
destination: "ansible_env_ready.yml"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "ansible-playbook ansible_env_ready.yml"
end
endansible_env_ready.yml
---
- name: Setup for the Ansible's Environment
hosts: localhost
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: Add "/etc/ansible/hosts"
blockinfile:
path: /etc/ansible/hosts
block: |
[vyos]
192.168.1.51 ansible_connection=network_cli ansible_network_os=vyos
192.168.1.52 ansible_connection=network_cli ansible_network_os=vyos
- name: Generate sshkey
become: yes
become_user: vagrant
shell: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "ssh-keyscan 192.168.1.51 >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts"
- "ssh-keyscan 192.168.1.52 >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts"
- name: Create vim env's directories & files
shell: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "mkdir -p /home/vagrant/.vim/autoload /home/vagrant/.vim/bundle"
- "touch /home/vagrant/.vimrc"
- "touch /home/vagrant/.bashrc"
- name: Install vim-enhanced
yum:
name: vim-enhanced
state: present
- name: Install git
yum:
name: git
state: present
- name: Download pathogen.vim
shell: "curl -fLo /home/vagrant/.vim/autoload/pathogen.vim
https://tpo.pe/pathogen.vim"
- name: Git clone vim-ansible-yaml
git:
repo: https://github.com/chase/vim-ansible-yaml.git
dest: /home/vagrant/.vim/bundle/vim-ansible-yaml
- name: Configure vimrc
lineinfile:
path: /home/vagrant/.vimrc
line: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "set number"
- "execute pathogen#infect()"
- "syntax on"
- name: Configure Bashrc
lineinfile:
path: /home/vagrant/.bashrc
line: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "alias ans='ansible'"
- "alias anp='ansible-playbook'"초반에 게스트 관련된 뭔가를 설치 해야된다고 본거 같은데...
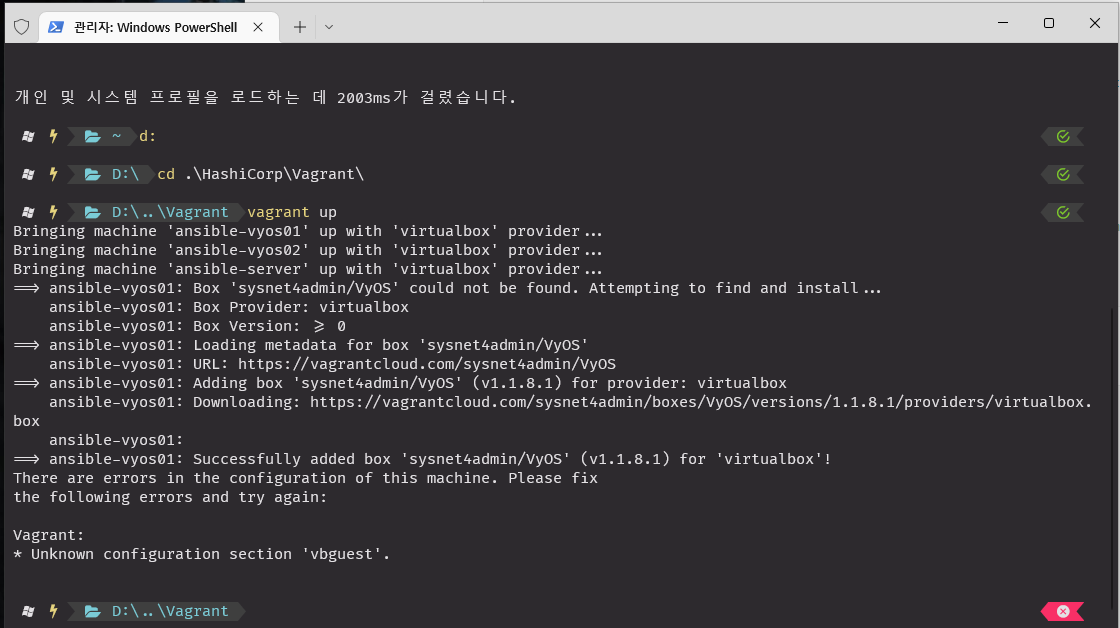
플러그인 설치 후 재시도
vagrant plugin install vagrant-vbguest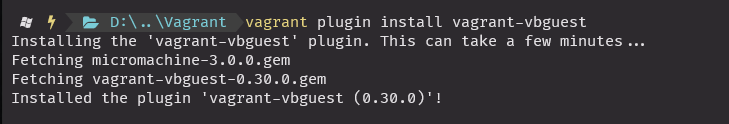
vagrant ssh ansible-server
핑체크
ans vyos -m ping -k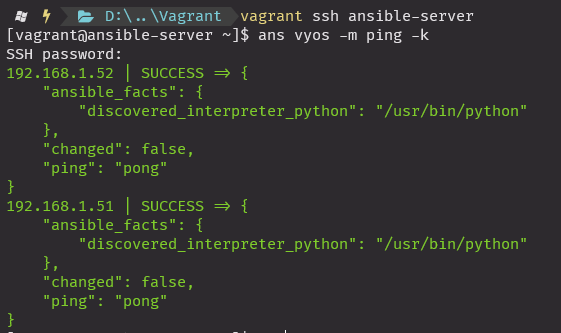
uname -r
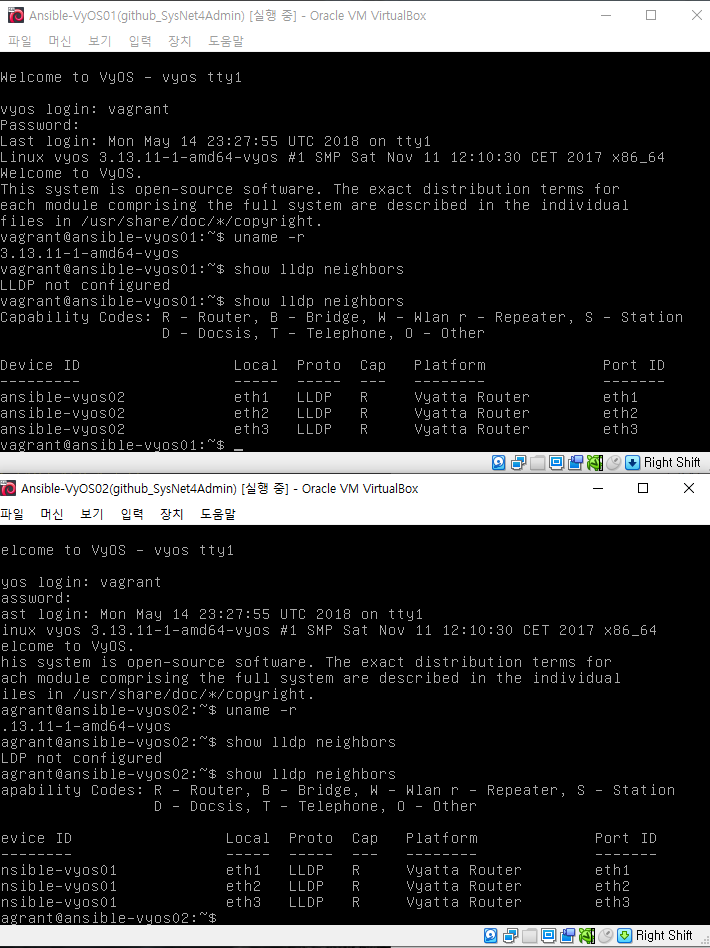
show lldp neighbors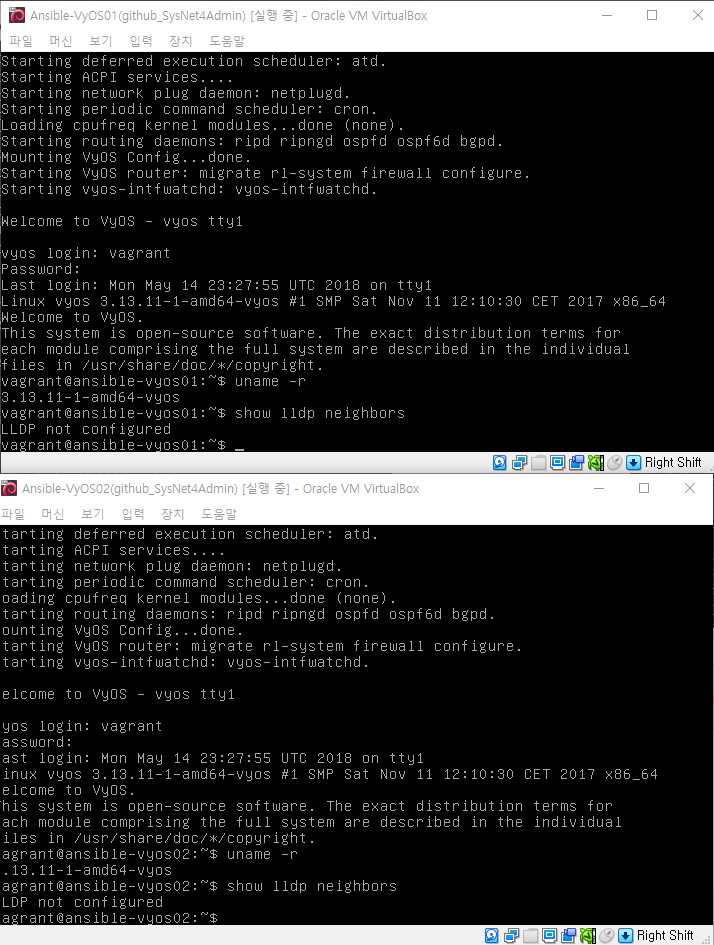
lldp 설정
vyos_lldp.yml -k
---
- name: Config lldp service
hosts: vyos
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: enable lldp service
vyos_lldp:
state: present
- name: save running-config
vyos_config:
save: yesanp vyos_lldp.yml -k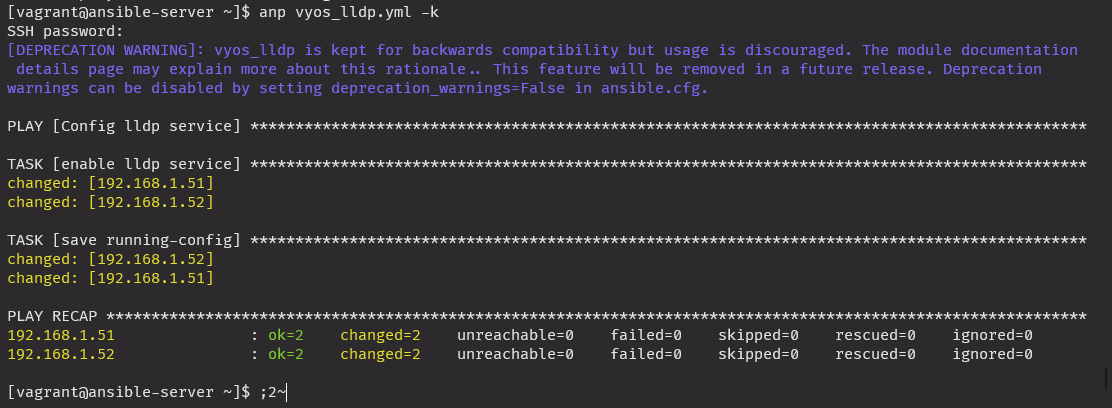
설치 후 show lldp neighbors 정상 실행
호스트 네임 변경
리붓 후 호스트 네임 초기화
vyos_hostname.yml
---
- name: Change&set the hostname
hosts: vyos
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: hostname for ansible-vyos01
delegate_to: 192.168.1.51
run_once: true
vyos_system:
host_name: ansible-vyosA
- name: hostname for ansible-vyos02
delegate_to: 192.168.1.52
run_once: true
vyos_system:
host_name: ansible-vyosB
- name: save running-config
vyos_config:
save: yesanp vyos_hostname.yml -k적용 후 재부팅 후에도 정상적으로 호스트 네임 유지 확인
컨피그 확인시에도 적용
show configuration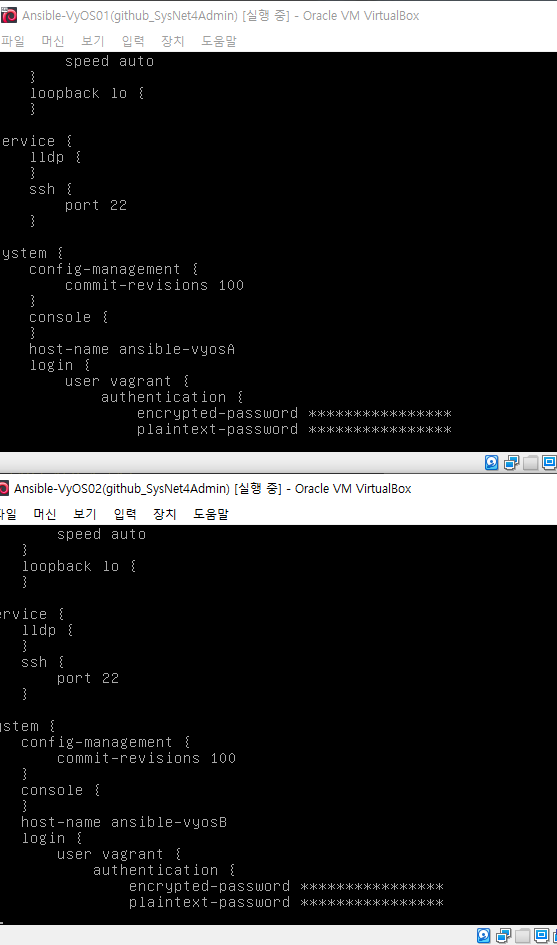
링크 어그리게이션 설정
vyos_bond.yml
---
- name: Config link Aggregation
hosts: vyos
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: make a bond interface
vyos_linkagg:
name: bond0
members:
- eth2
- eth3
mode: 802.3ad
- name: save running-config
vyos_config:
save: yes실행
anp vyos_bond.yml -k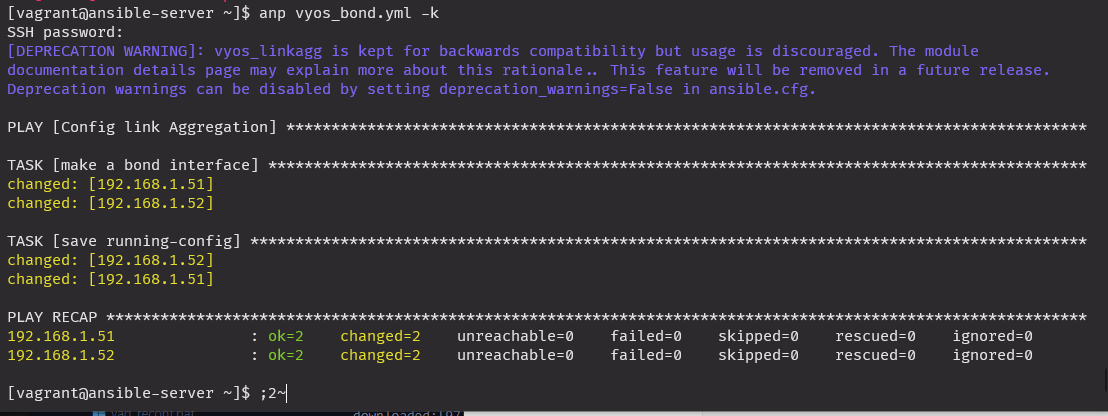
본딩확인
show interfaces bonding bond0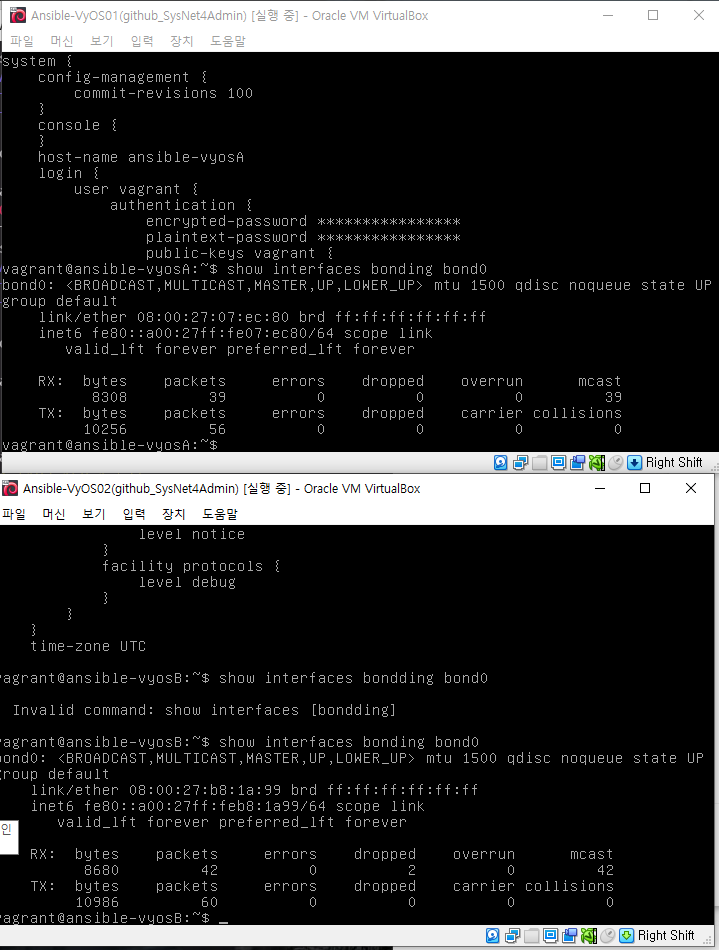
어그리게이션 확인
monitor interfaces ethernet eth2 traffic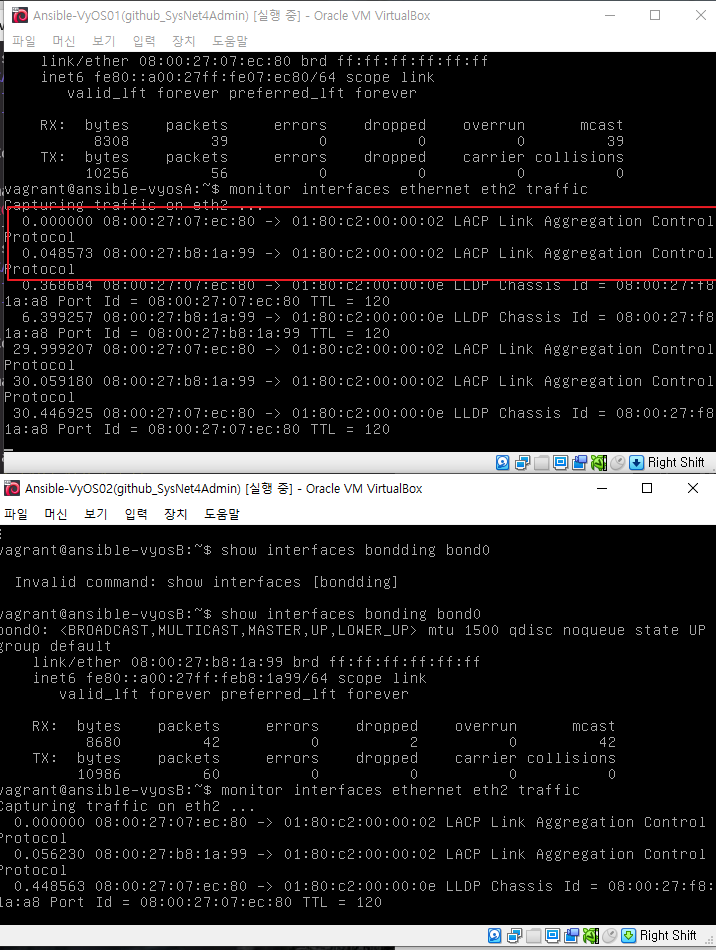
맥어드레스확인 / 위에 통신하는 맥주소
show interfaces ethernet eth2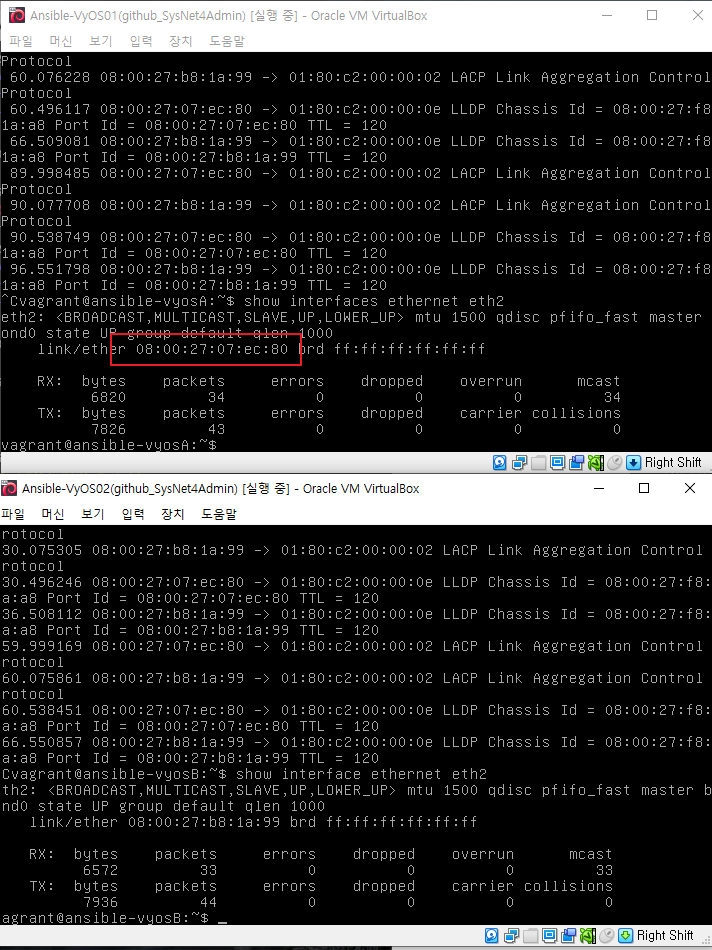
본딩확인
show conf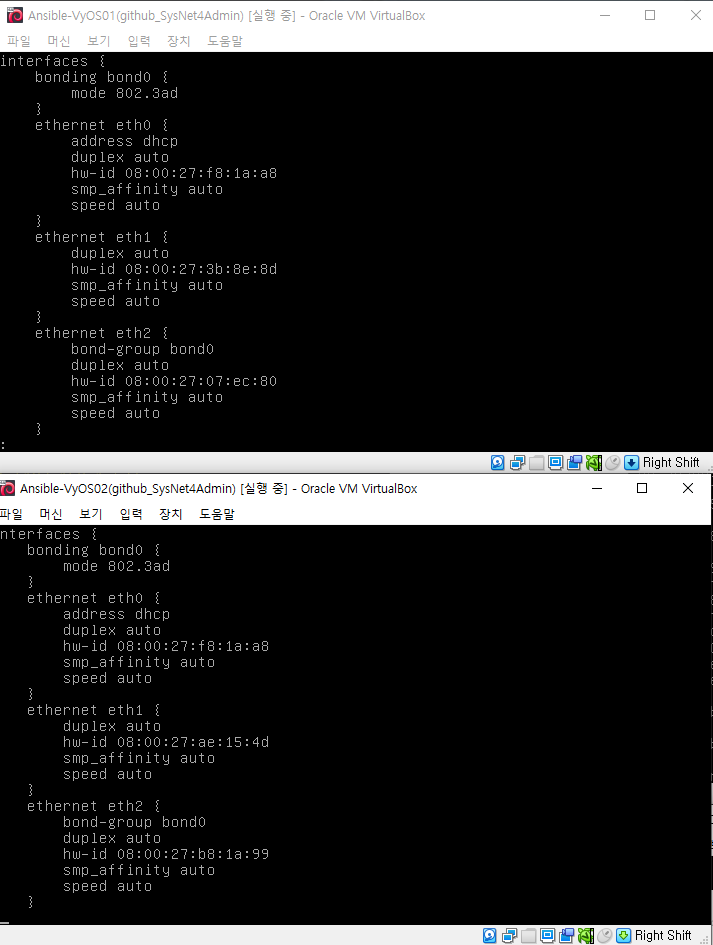
Cumulus를 다루기
앤서블을 통해서 다룰 수 있는 네트워크 운영체제
vagrantfile
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
#===============#
# Cumulus nodes #
#===============#
#Ansible-Cumulus01
config.vm.define "ansible-cl01" do |cl|
cl.vm.box = "CumulusCommunity/cumulus-vx"
cl.vm.box_version = "3.6.0"
cl.vm.box_check_update = false
cl.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Cumulus01(github_SysNet4Admin)"
vb.customize ['modifyvm', :id, '--macaddress1', '080027000061']
vb.customize ['modifyvm', :id, '--natnet1', '10.0.61.0/24']
end
cl.vm.host_name = "ansible-cl01"
cl.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.61"
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp2", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp3", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp4", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60061, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cl.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
end
#Ansible-Cumulus02
config.vm.define "ansible-cl02" do |cl|
cl.vm.box = "CumulusCommunity/cumulus-vx"
cl.vm.box_version = "3.6.0"
cl.vm.box_check_update = false
cl.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Cumulus02(github_SysNet4Admin)"
vb.customize ['modifyvm', :id, '--macaddress1', '080027000062']
vb.customize ['modifyvm', :id, '--natnet1', '10.0.62.0/24']
end
cl.vm.host_name = "ansible-cl02"
cl.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.62"
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp2", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp3", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp4", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60062, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cl.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
end
#Ansible-Cumulus03
config.vm.define "ansible-cl03" do |cl|
cl.vm.box = "CumulusCommunity/cumulus-vx"
cl.vm.box_version = "3.6.0"
cl.vm.box_check_update = false
cl.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Cumulus03(github_SysNet4Admin)"
vb.customize ['modifyvm', :id, '--macaddress1', '080027000063']
vb.customize ['modifyvm', :id, '--natnet1', '10.0.63.0/24']
end
cl.vm.host_name = "ansible-cl03"
cl.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.63"
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp2", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp3", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp4", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60063, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cl.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
end
#Ansible-Cumulus04
config.vm.define "ansible-cl04" do |cl|
cl.vm.box = "CumulusCommunity/cumulus-vx"
cl.vm.box_version = "3.6.0"
cl.vm.box_check_update = false
cl.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Cumulus04(github_SysNet4Admin)"
vb.customize ['modifyvm', :id, '--macaddress1', '080027000064']
vb.customize ['modifyvm', :id, '--natnet1', '10.0.64.0/24']
end
cl.vm.host_name = "ansible-cl04"
cl.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.64"
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp2", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp3", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "private_network", virtualbox__intnet: "swp4", auto_config: false
cl.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60064, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cl.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
end
#================#
# Ansible Server #
#================#
config.vm.define "ansible-server" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "Ansible-Server(github_SysNet4Admin)"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-server"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.60"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60010, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "yum install epel-release -y"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "yum install ansible -y"
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ansible_env_ready.yml",
destination: "ansible_env_ready.yml"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "ansible-playbook ansible_env_ready.yml"
end
endansible_env_ready.yml
---
- name: Setup for the Ansible's Environment
hosts: localhost
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: Add "/etc/ansible/hosts"
blockinfile:
path: /etc/ansible/hosts
block: |
[spine]
192.168.1.61
192.168.1.62
[leaf]
192.168.1.63
192.168.1.64
[cl:children]
spine
leaf
- name: Generate sshkey
become: yes
become_user: vagrant
shell: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "ssh-keyscan 192.168.1.61 >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts"
- "ssh-keyscan 192.168.1.62 >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts"
- "ssh-keyscan 192.168.1.63 >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts"
- "ssh-keyscan 192.168.1.64 >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts"
- name: Create vim env's directories & files
shell: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "mkdir -p /home/vagrant/.vim/autoload /home/vagrant/.vim/bundle"
- "touch /home/vagrant/.vimrc"
- "touch /home/vagrant/.bashrc"
- name: Install vim-enhanced
yum:
name: vim-enhanced
state: present
- name: Install git
yum:
name: git
state: present
- name: Download pathogen.vim
shell: "curl -fLo /home/vagrant/.vim/autoload/pathogen.vim
https://tpo.pe/pathogen.vim"
- name: Git clone vim-ansible-yaml
git:
repo: https://github.com/chase/vim-ansible-yaml.git
dest: /home/vagrant/.vim/bundle/vim-ansible-yaml
- name: Configure vimrc
lineinfile:
path: /home/vagrant/.vimrc
line: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "set number"
- "execute pathogen#infect()"
- "syntax on"
- name: Configure Bashrc
lineinfile:
path: /home/vagrant/.bashrc
line: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "alias ans='ansible'"
- "alias anp='ansible-playbook'"ans cl -m ping -k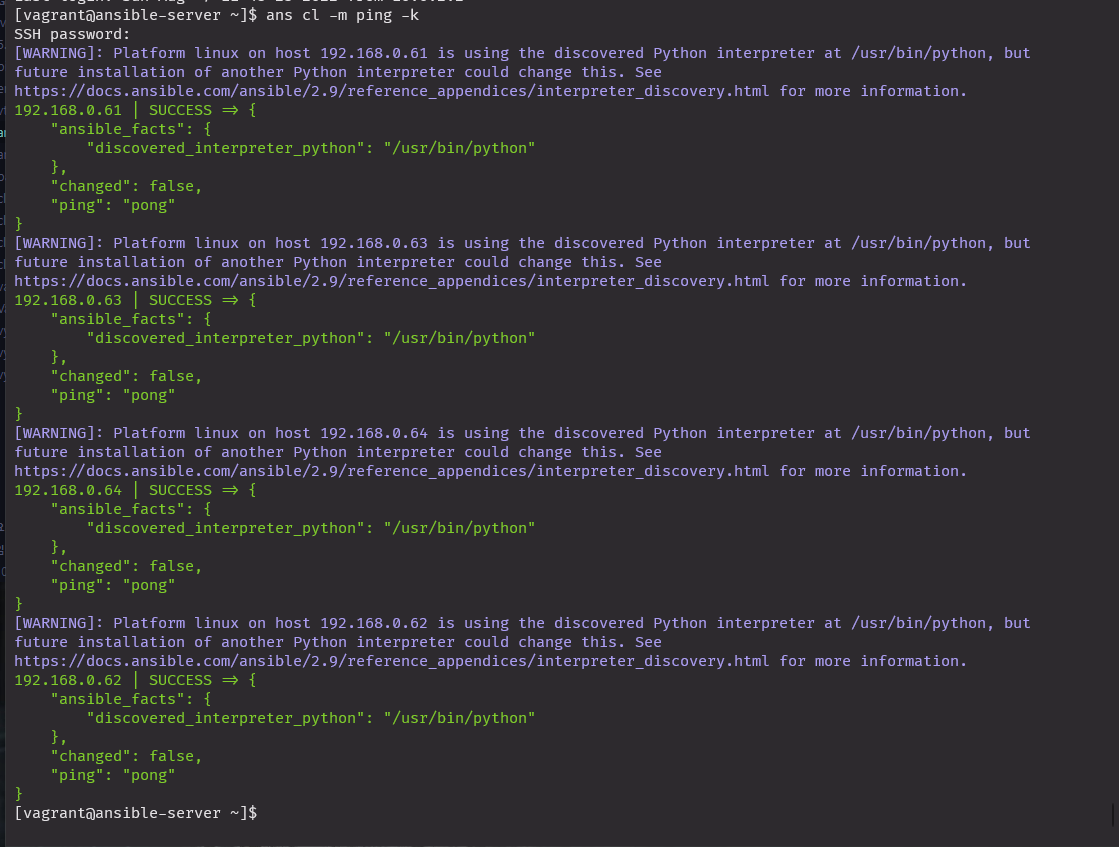
호스트 네임 변경
cl_hostname.yml
---
- name: Change the hostname
hosts: cl
gather_facts: no
become: yes
tasks:
- name: hostname for ansible-cl01
delegate_to: 192.168.0.61
run_once: true
nclu:
commands:
- add hostname ansible-spineA
atomic: true
- name: hostname for ansible-cl02
delegate_to: 192.168.0.62
run_once: true
nclu:
commands:
- add hostname ansible-spineB
atomic: true
- name: hostname for ansible-cl03
delegate_to: 192.168.0.63
run_once: true
nclu:
commands:
- add hostname ansible-leafA
atomic: true
- name: hostname for ansible-cl04
delegate_to: 192.168.0.64
run_once: true
nclu:
commands:
- add hostname ansible-leafB
atomic: true
- name: lldp service restart
service:
name: lldpd
state: restartedLLDP 확인
net show lldp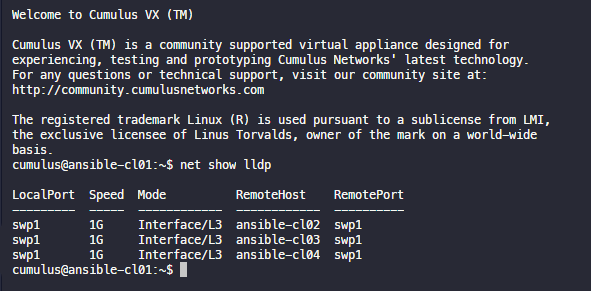
anp cl_hostname.yml -k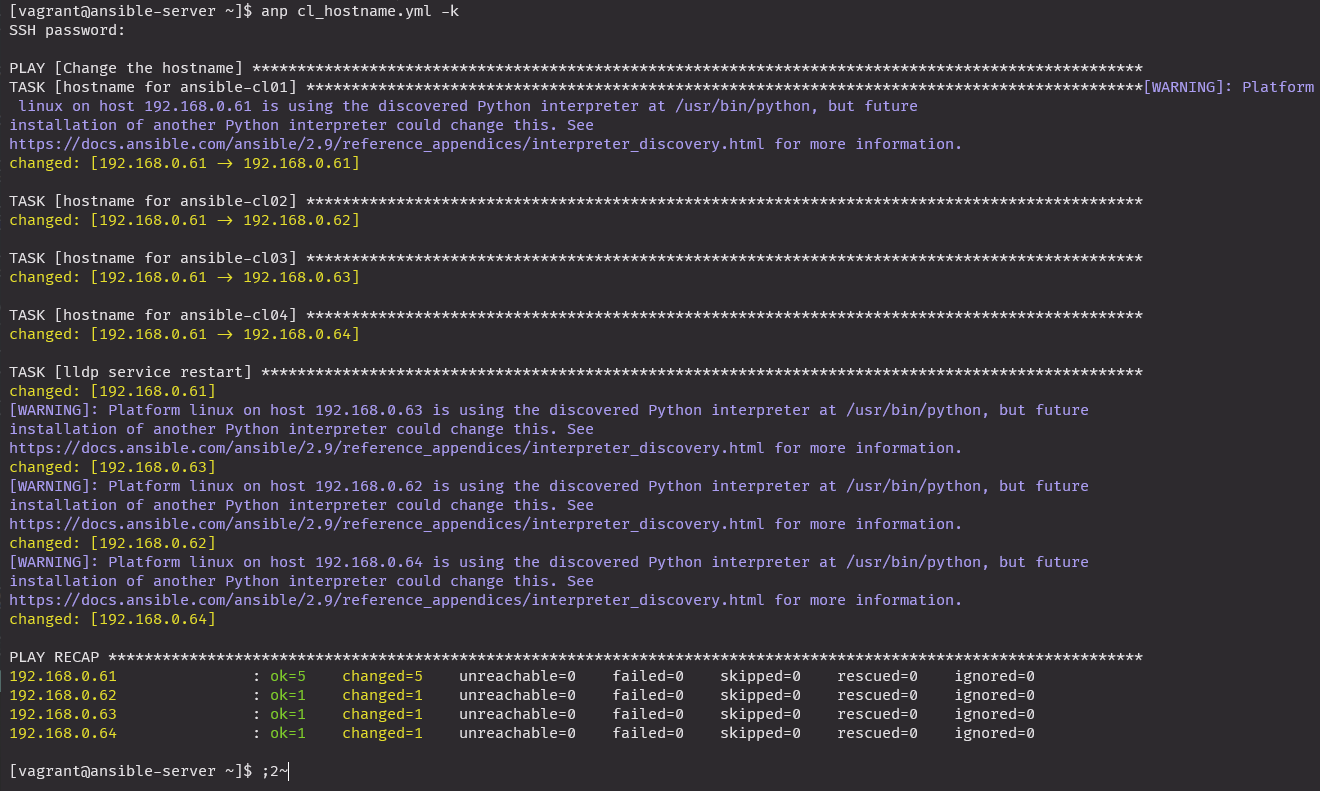
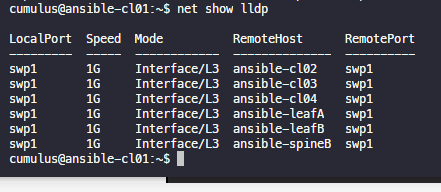
기존 정보는 남아있으나 곧 사라짐...(240초)
Cumulus의 spine 노드간 peer-link 구성하기
cl_peerlink.yml
---
- name: Config switch virtual interface(SVI) with bonding
hosts: spine
gather_facts: no
become: yes
tasks:
- name: put in config
nclu:
commands:
- add bond bond0 bond slaves swp2,3
- add bridge
- add bridge bridge ports bond0
- add bridge bridge vids 10
- add bridge bridge pvid 1
atomic: true
- name: setup ip for spineA's SVI
delegate_to: 192.168.0.61
run_once: true
nclu:
commands:
- add vlan 10 ip address 10.0.10.61/24
atomic: true
- name: setup ip for spineB's SVI
delegate_to: 192.168.0.62
run_once: true
nclu:
commands:
- add vlan 10 ip address 10.0.10.62/24
atomic: true아이피 오류로 수정했다가 적용
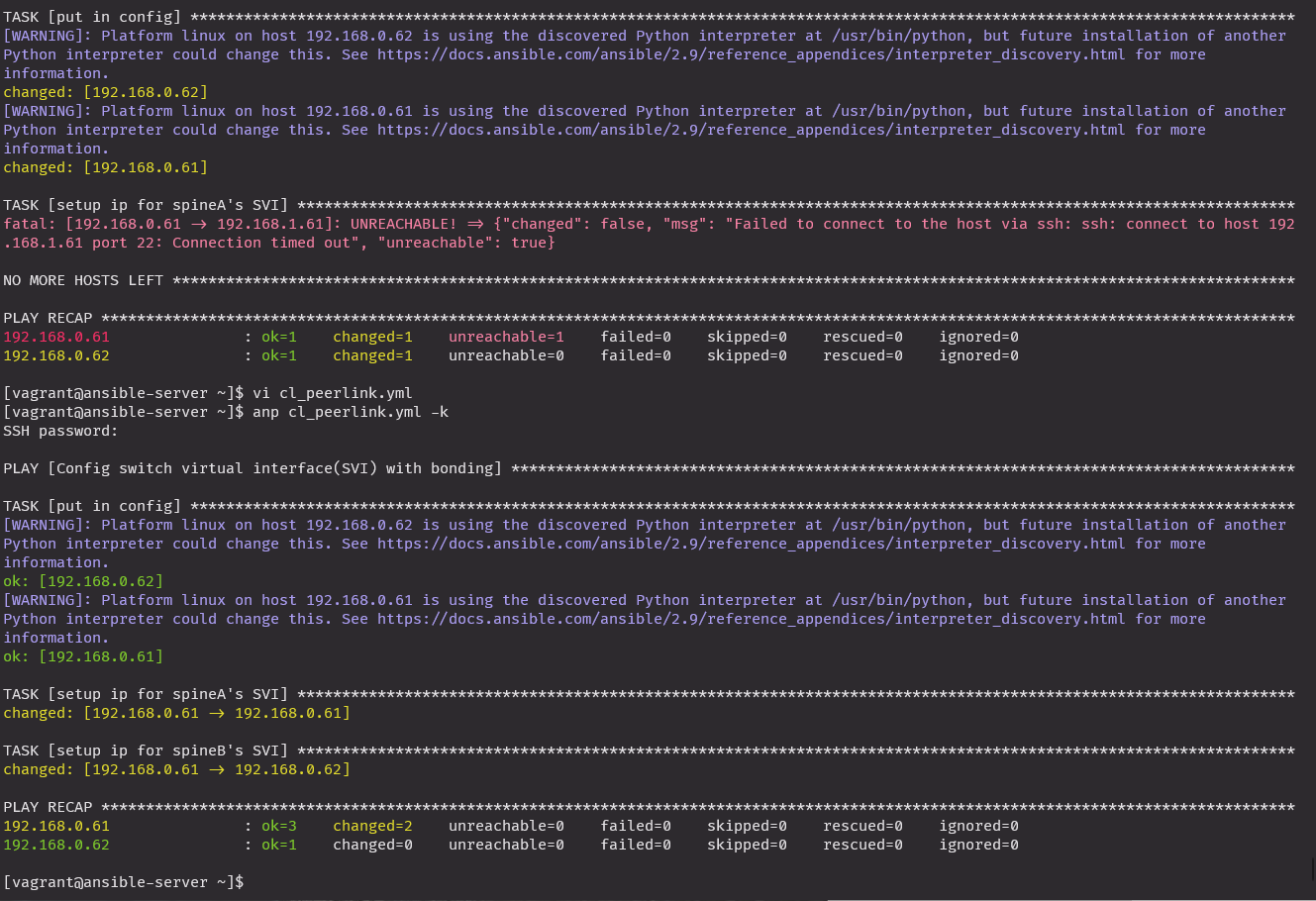
ping 10.0.10.62
arp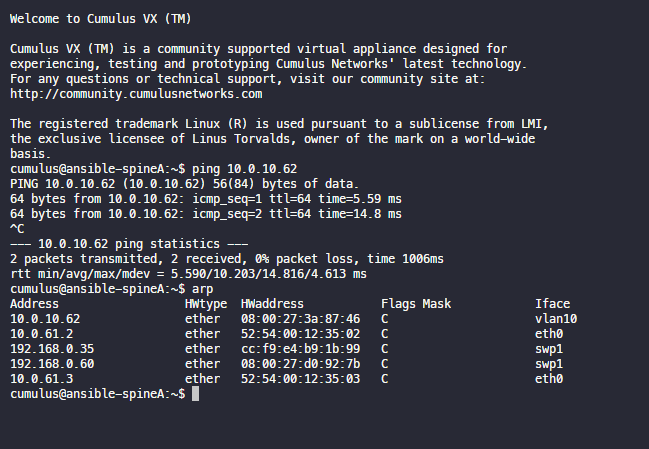
net show configuration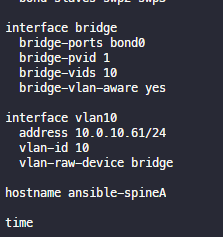
구성변경 및 팬딩 확인
net del bridge bridge vids 10
net add bridge birdge vids 100
net pending
적용
net commit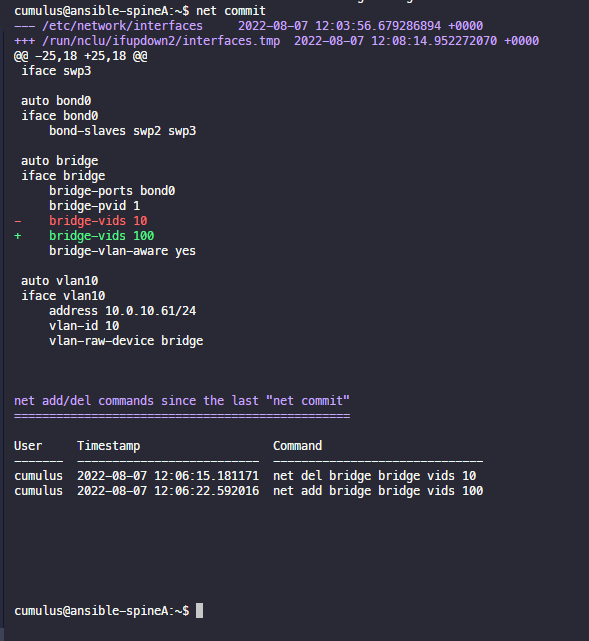
vlan 변경에 따른 전송 불가

Cumulus 노드 간에 OSPF를 구성 하기
OSPF = 최단 우선 경로 (Open Shortest Path First)
cl_int.yml
---
- name: Config interface for spineA
hosts: 192.168.0.61
gather_facts: no
become: yes
tasks:
- name: put in config
nclu:
commands:
- add interface swp4 ip address 10.0.101.61/24
atomic: true
- name: Config interface for spineB
hosts: 192.168.0.62
gather_facts: no
become: yes
tasks:
- name: put in config
nclu:
commands:
- add interface swp4 ip address 10.0.102.62/24
atomic: true
- name: Config interface for leafA
hosts: 192.168.0.63
gather_facts: no
become: yes
tasks:
- name: put in config
nclu:
commands:
- add interface swp4 ip address 10.0.101.63/24
atomic: true
- name: Config interface for leafB
hosts: 192.168.0.64
gather_facts: no
become: yes
tasks:
- name: put in config
nclu:
commands:
- add interface swp4 ip address 10.0.102.64/24
atomic: truecl_ospf.yml
---
- name: Config OSPF for spineA
hosts: 192.168.0.61
gather_facts: no
become: yes
tasks:
- name: put in config
nclu:
commands:
- add ospf router-id 0.0.0.61
- add ospf network 10.0.0.0/16 area 0.0.0.0
atomic: true
- name: Config OSPF for spineB
hosts: 192.168.0.62
gather_facts: no
become: yes
tasks:
- name: put in config
nclu:
commands:
- add ospf router-id 0.0.0.62
- add ospf network 10.0.0.0/16 area 0.0.0.0
atomic: true
- name: Config OSPF for leafA
hosts: 192.168.0.63
gather_facts: no
become: yes
tasks:
- name: put in config
nclu:
commands:
- add ospf router-id 0.0.0.63
- add ospf network 10.0.0.0/16 area 0.0.0.0
atomic: true
- name: Config OSPF for leafB
hosts: 192.168.0.64
gather_facts: no
become: yes
tasks:
- name: put in config
nclu:
commands:
- add ospf router-id 0.0.0.64
- add ospf network 10.0.0.0/16 area 0.0.0.0
atomic: trueanp cl_int.yml -k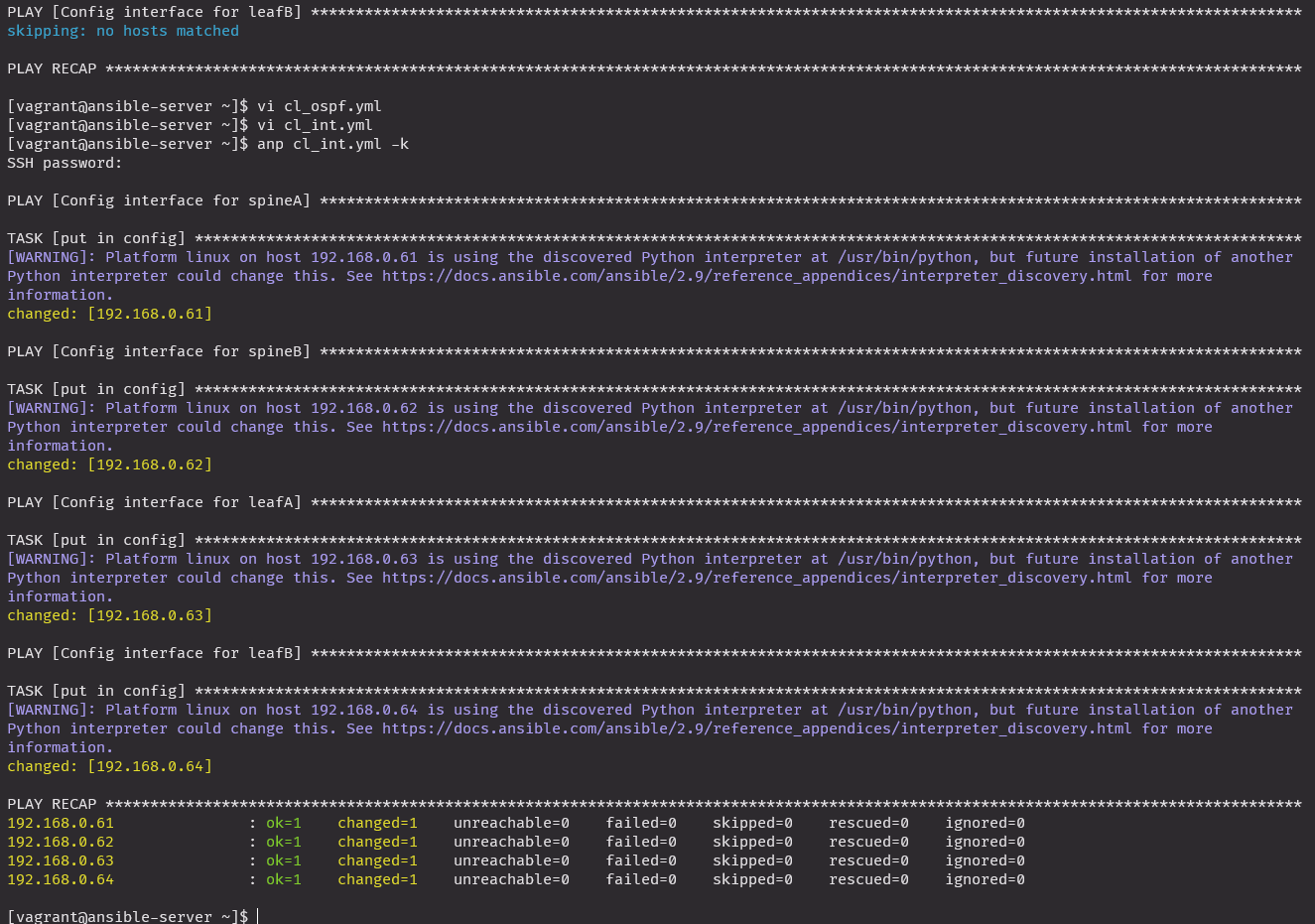
net show interface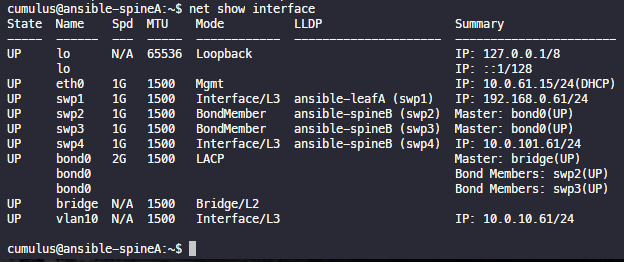
ping 10.0.101.61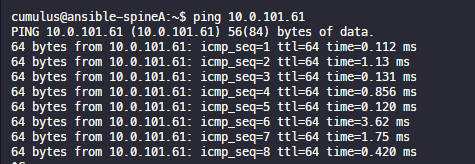
ping 10.0.102.64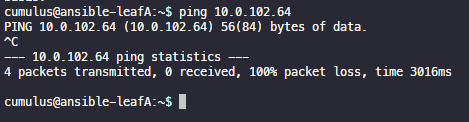
net show route ipv4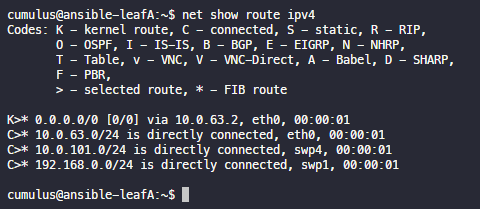
OSPF
anp cl_ospf.yml -k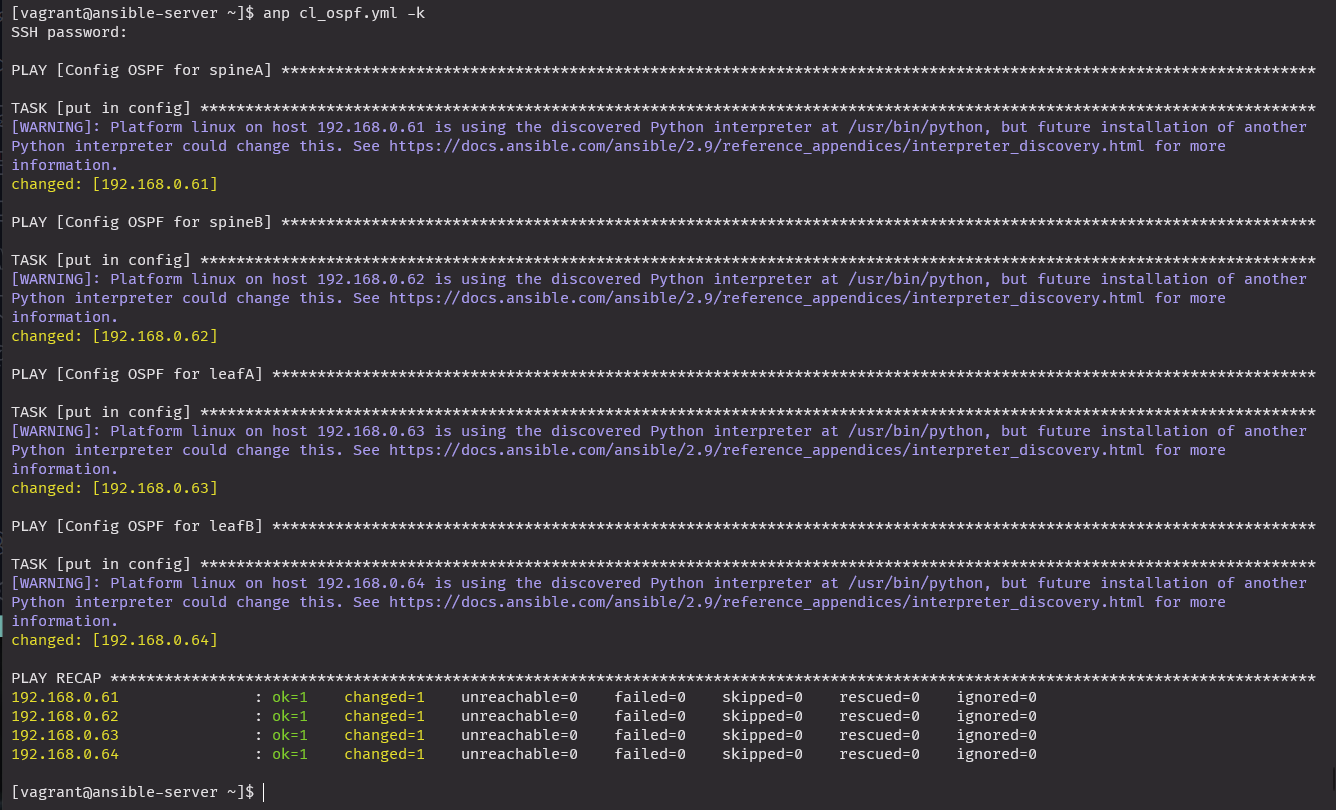
[우아하게 앤서블] Chapter 4 - 리눅스와 윈도우를 앤서블을 통해서 관리
참고사항
책과는 다르게 Hyper-V 환경에서 진행하고 있습니다. (책은 VirtualBox기준)
공부를 매주 토요일마다 진행하고 있는데 지난주에 일이 바빠서...한주를 쉬었더니 완전 까먹은 상태로 다시 접속을 시도 했으나 접속이 안되는 증상이 발생을 해서..
...다시 설치중...책에는 재설정하는 컨피그 방법을 가이드(따봉입니다.) 하고 있어서 해당부분을 진행중이었는데
설치 하던 와중에 vagrant를 통해서 접속을 했었다는것이 기억남...
재설치를 완료하여 진행했더니..접속이 잘됩니다. ㅎㅎㅎ

nginx 설치 및 삭제하기
nginx_install.yml
---
- name: Install nginx on CentOS
hosts: CentOS
gather_facts: no
become: yes
tasks:
- name: install epel-release
yum: name=epel-release state=latest
- name: install nginx web server
yum: name=nginx state=present
- name: upload default index.html for web server
get_url: url=https://www.nginx.com dest=/usr/share/nginx/html/ mode=0644
- name: start nginx web server
service: name=nginx state=startednginx_remove.yml
---
- name: Remove nginx on CentOS
hosts: CentOS
gather_facts: no
become: yes
tasks:
- name: remove epel-release
yum: name=epel-release state=absent
- name: remove nginx web server
yum: name=nginx state=absent인스톨 명령 후 실행 후 사이트 정상접속 확인
anp nginx_install.yml -k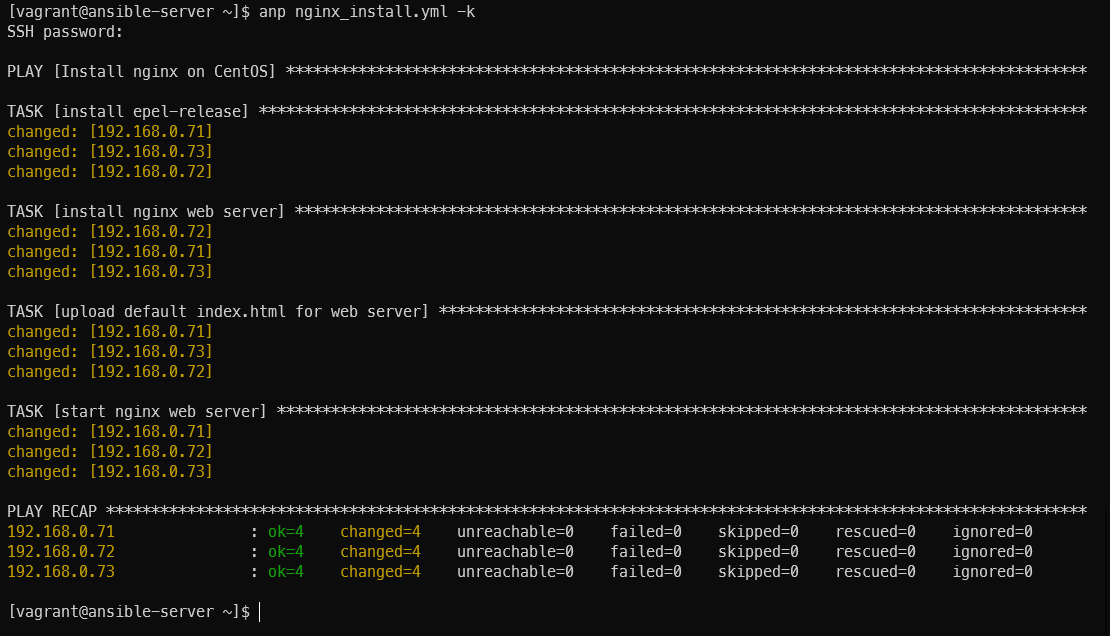

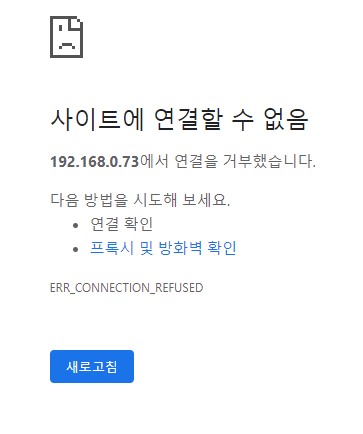
사이트 삭제
anp nginx_remove.yml -k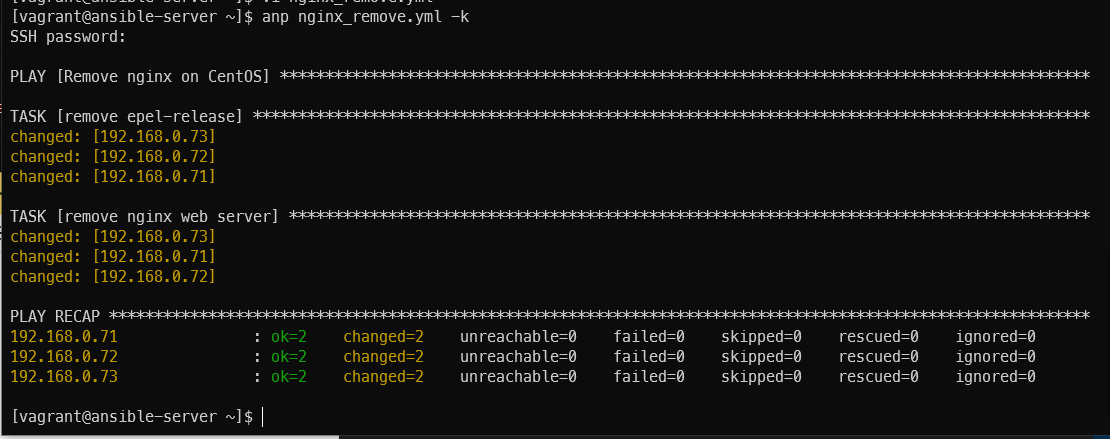
현재 계정 실행은 vagrant로 실행하고 있기 때문에 sudo 권한이 필요함, 따라서 become라는 구문을 통해서 실행 될 테스크들의 권한을 높여야 함.
become: yes현재 시간 확인 (UTC 기준)
노드들도 확인
timedatectl
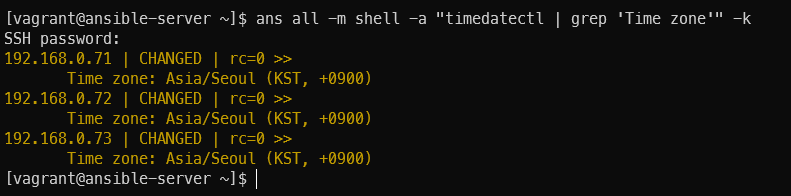
ans all -m shell -a "timedatectl | grep 'Time zone'" -k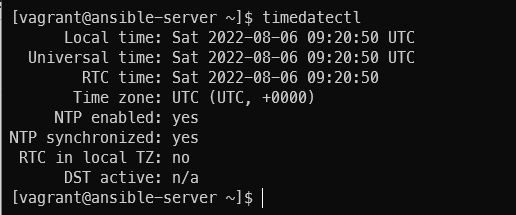
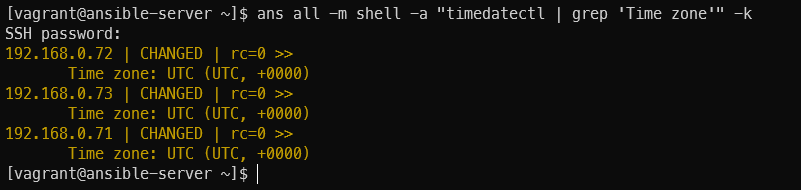
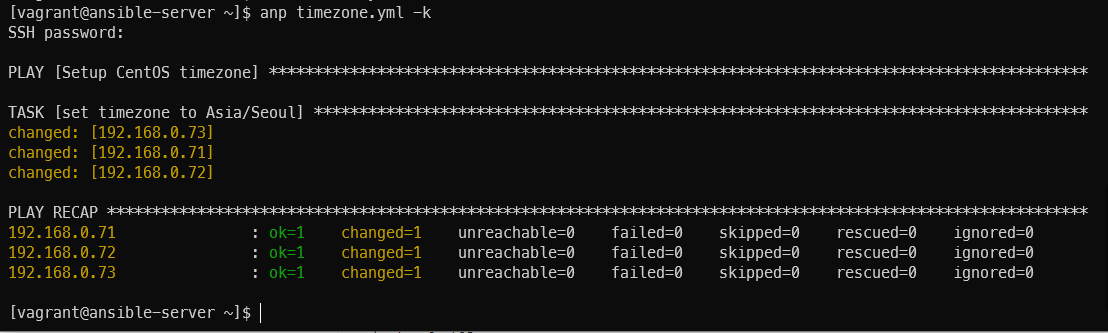
타임존 한국으로 변경 작업 후 확인
timezone.yml
---
- name: Setup CentOS timezone
hosts: CentOS
gather_facts: no
become: yes
tasks:
- name: set timezone to Asia/Seoul
timezone: name=Asia/Seoulanp timezone.yml -k
앤서블 서버 시간 대 변경
심볼링 링크 -s : 심블록 링크 파일 생성, -f 지정된 위치에 파일이 있다면, 지우고 새로 생성(force)
sudo ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Seoul /etc/localtime
timedatectl | grep 'Time zone'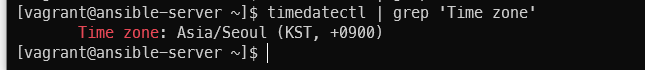
NFS 서버와 클라이언트 구성하기
nfs.yml
---
- name: Setup for nfs server
hosts: localhost
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: make nfs_shared directory
file:
path: /home/vagrant/nfs_shared
state: directory
mode: 0777
- name: configure /etc/exports
become: yes
lineinfile:
path: /etc/exports
line: /home/vagrant/nfs_shared 192.168.0.0/24(rw,sync)
- name: nfs service restart
become: yes
service:
name: nfs
state: restarted
- name: Setup for nfs clients
hosts: CentOS
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: make nfs_client directory
file:
path: /home/vagrant/nfs
state: directory
- name: mount point directory as client
become: yes
mount:
path: /home/vagrant/nfs
src: 192.168.0.70:/home/vagrant/nfs_shared
fstype: nfs
opts: nfsvers=3
state: mountednfs 설정 적용
anp nfs.yml -k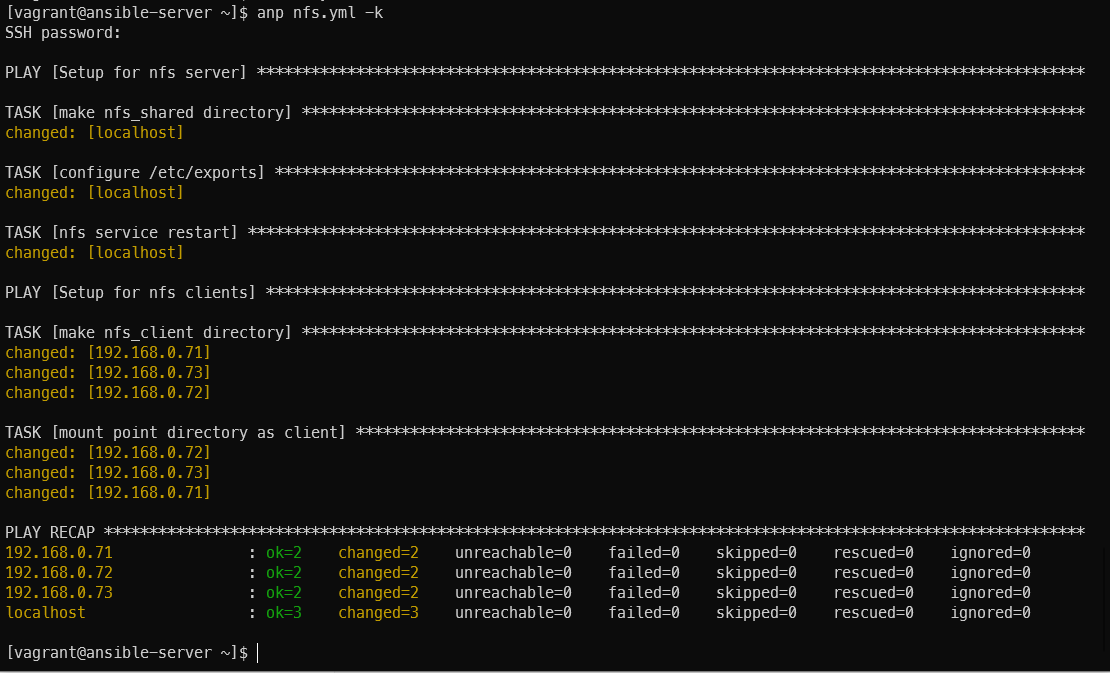
nfs 서버 설정 확인
cat /etc/exports
각 노드의 nfs 공유 디렉터리에 각 호스트 이름을 기록
ans all -m shell -a "cat /etc/hostname | xargs -i touch ./nfs/{}" -k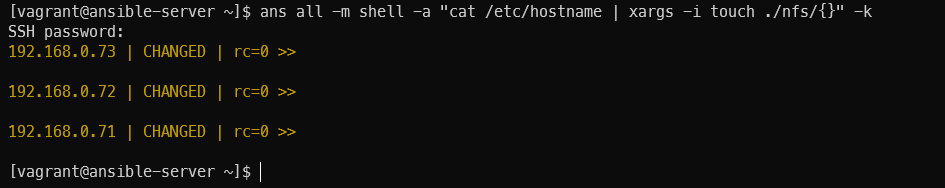
확인
ls ./nfs_shared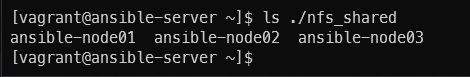
노드에서도 nfs 작동 확인
ssh vagrant@192.160.0.71
ls ./nfs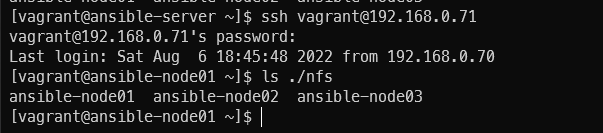
우분투 추가하기
vagrantfile
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
#==============#
# CentOS nodes #
#==============#
#Ansible-Node01
config.vm.define "ansible-node01" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node01"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node01"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-node01.sh",
destination: "ip-node01.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-node01.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "bash_ssh_conf_4_CentOS.sh"
end
#Ansible-Node02
config.vm.define "ansible-node02" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node02"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node02"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-node02.sh",
destination: "ip-node02.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-node02.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "bash_ssh_conf_4_CentOS.sh"
end
#Ansible-Node03
config.vm.define "ansible-node03" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node03"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node03"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-node03.sh",
destination: "ip-node03.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-node03.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "bash_ssh_conf_4_CentOS.sh"
end
#==============#
# Ubuntu nodes #
#==============#
#Ansible-Node04
config.vm.define "ansible-node04" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node04"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node04"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-node04.sh",
destination: "ip-node04.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-node04.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
end
#Ansible-Node05
config.vm.define "ansible-node05" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node05"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node05"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-node05.sh",
destination: "ip-node05.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-node05.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
end
#Ansible-Node06
config.vm.define "ansible-node06" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node06"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node06"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-node06.sh",
destination: "ip-node06.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-node06.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
end
#================#
# Ansible Server #
#================#
config.vm.define "ansible-server" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-Server"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-server"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-server.sh",
destination: "ip-server.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-server.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "yum install epel-release -y && yum install ansible -y"
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ansible_env_ready.yml",
destination: "ansible_env_ready.yml"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "ansible-playbook ansible_env_ready.yml"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "add_ssh_auth.sh", privileged: false
end
end앤서블환경구성 아뮬
ansible_env_ready.yml
---
- name: Setup for the Ansible's Environment
hosts: localhost
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: Add "/etc/ansible/hosts"
blockinfile:
path: /etc/ansible/hosts
block: |
[CentOS]
192.168.0.71
192.168.0.72
192.168.0.73
[Ubuntu]
192.168.0.74
192.168.0.75
192.168.0.76
- name: Install sshpass for Authentication
yum:
name: sshpass
state: present
- name: Create vim env's directories & files
shell: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "mkdir -p /home/vagrant/.vim/autoload /home/vagrant/.vim/bundle"
- "touch /home/vagrant/.vimrc"
- "touch /home/vagrant/.bashrc"
- name: Install vim-enhanced
yum:
name: vim-enhanced
state: present
- name: Install git
yum:
name: git
state: present
- name: Download pathogen.vim
shell: "curl -fLo /home/vagrant/.vim/autoload/pathogen.vim
https://tpo.pe/pathogen.vim"
- name: Git clone vim-ansible-yaml
git:
repo: https://github.com/chase/vim-ansible-yaml.git
dest: /home/vagrant/.vim/bundle/vim-ansible-yaml
- name: Configure vimrc
lineinfile:
path: /home/vagrant/.vimrc
line: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "set number"
- "execute pathogen#infect()"
- "syntax on"
- name: Configure Bashrc
lineinfile:
path: /home/vagrant/.bashrc
line: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "alias ans='ansible'"
- "alias anp='ansible-playbook'"ssh 인증 추가
add_ssh_auth.sh
#! /usr/bin/env bash
#ssh key 생성
sshpass -p vagrant ssh -T -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no vagrant@192.168.0.71
sshpass -p vagrant ssh -T -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no vagrant@192.168.0.72
sshpass -p vagrant ssh -T -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no vagrant@192.168.0.73
sshpass -p vagrant ssh -T -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no vagrant@192.168.0.74
sshpass -p vagrant ssh -T -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no vagrant@192.168.0.75
sshpass -p vagrant ssh -T -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no vagrant@192.168.0.76기존 앤서블 테스트 환경 삭제
vagrant destroy -f
우분투 추가
vagrant up를 했으나 오류가 나서 확인해보니 vagrant 는 우분투 기반에 대해서는 virtualbox로만 지원하는것으로 확인
책 내용 확인 시 CentOS 진행하던 것과 동일해서 우분투 부분 실습은 제외하는것으로 우선 진행
윈도우를 다루기
윈도우 노두 추가한 베어그런트파일
vagrantfile
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
#==============#
# CentOS nodes #
#==============#
#Ansible-Node01
config.vm.define "ansible-node01" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node01"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node01"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-node01.sh",
destination: "ip-node01.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-node01.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "bash_ssh_conf_4_CentOS.sh"
end
#Ansible-Node02
config.vm.define "ansible-node02" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node02"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node02"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-node02.sh",
destination: "ip-node02.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-node02.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "bash_ssh_conf_4_CentOS.sh"
end
#Ansible-Node03
config.vm.define "ansible-node03" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node03"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node03"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-node03.sh",
destination: "ip-node03.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-node03.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "bash_ssh_conf_4_CentOS.sh"
end
#================#
# Windows Server #
#================#
#Ansible-Node03
config.vm.define "ansible-node07" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "mwrock/Windows2016"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node07"
hv.customize ['modifyvm', :id, '--clipboard', 'bidirectional']
hv.gui = false
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node07"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60017, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "netsh advfirewall set allprofiles state off"
end
#================#
# Ansible Server #
#================#
config.vm.define "ansible-server" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-Server"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-server"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-server.sh",
destination: "ip-server.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-server.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "yum install epel-release -y && yum install ansible -y"
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ansible_env_ready.yml",
destination: "ansible_env_ready.yml"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "ansible-playbook ansible_env_ready.yml"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "add_ssh_auth.sh", privileged: false
end
end앤서블 환경설정 파일
ansible_env_ready.yml
---
- name: Setup for the Ansible's Environment
hosts: localhost
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: Add "/etc/ansible/hosts"
blockinfile:
path: /etc/ansible/hosts
block: |
[CentOS]
192.168.0.71
192.168.0.72
192.168.0.73
[Windows]
172.168.0.77
- name: Install sshpass for Authentication
yum:
name: sshpass
state: present
- name: Create vim env's directories & files
shell: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "mkdir -p /home/vagrant/.vim/autoload /home/vagrant/.vim/bundle"
- "touch /home/vagrant/.vimrc"
- "touch /home/vagrant/.bashrc"
- name: Install vim-enhanced
yum:
name: vim-enhanced
state: present
- name: Install git
yum:
name: git
state: present
- name: Download pathogen.vim
shell: "curl -fLo /home/vagrant/.vim/autoload/pathogen.vim
https://tpo.pe/pathogen.vim"
- name: Git clone vim-ansible-yaml
git:
repo: https://github.com/chase/vim-ansible-yaml.git
dest: /home/vagrant/.vim/bundle/vim-ansible-yaml
- name: Configure vimrc
lineinfile:
path: /home/vagrant/.vimrc
line: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "set number"
- "execute pathogen#infect()"
- "syntax on"
- name: Configure Bashrc
lineinfile:
path: /home/vagrant/.bashrc
line: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "alias ans='ansible'"
- "alias anp='ansible-playbook'"
삭제
vagrant destroy -f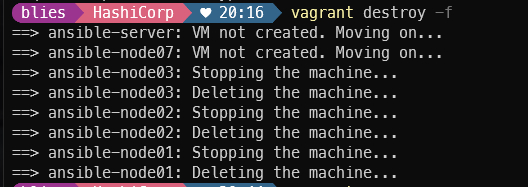
생성
vagrant up진행이 안되길래 뭔가했더니 생각치도 못한 용량부족..


우선 D드라이브로 설정 파일들을 다 옮기고
다시 설치 작업 진행
설치는 이슈 없는데...일단 아이피 변경은 또 안되는듯 하고..찾아봐야지..ㅠㅠ
서버에 직접 들어가서 netsh로 커맨드로 입력하면 우선 정상적으로 변경되는걸로는 확인은 해서 inline에 내용 추가 해서 테스트 진행
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
#==============#
# CentOS nodes #
#==============#
#Ansible-Node01
config.vm.define "ansible-node01" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node01"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node01"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-node01.sh",
destination: "ip-node01.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-node01.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "bash_ssh_conf_4_CentOS.sh"
end
#Ansible-Node02
config.vm.define "ansible-node02" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node02"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node02"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-node02.sh",
destination: "ip-node02.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-node02.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "bash_ssh_conf_4_CentOS.sh"
end
#Ansible-Node03
config.vm.define "ansible-node03" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node03"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node03"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-node03.sh",
destination: "ip-node03.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-node03.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "bash_ssh_conf_4_CentOS.sh"
end
#================#
# Windows Server #
#================#
#Ansible-Node03
config.vm.define "ansible-node07" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "mwrock/Windows2016"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node07"
hv.customize ['modifyvm', :id, '--clipboard', 'bidirectional']
hv.gui = false
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node07"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60017, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "netsh advfirewall set allprofiles state off"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "netsh interface ipv4 set address name='Ethernet' static 192.168.0.77 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.1"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "netsh interface ipv4 set dns name='Ethernet' static 8.8.8.8"
end
#================#
# Ansible Server #
#================#
config.vm.define "ansible-server" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-Server"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-server"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-server.sh",
destination: "ip-server.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-server.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "yum install epel-release -y && yum install ansible -y"
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ansible_env_ready.yml",
destination: "ansible_env_ready.yml"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "ansible-playbook ansible_env_ready.yml"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "add_ssh_auth.sh", privileged: false
end
end스크립트 돌면서 정상적으로 아이피 변경 확인은 했으나
이후 진행이 안되서 다시 확인중
윈도우 쪽은 우선 제외하고 진행
[우아하게 앤서블] Chapter 3 - 베이그런트를 이용해서 앤서블의 실습 환경 구성하기
참고사항
책과는 다르게 Hyper-V 환경에서 진행하고 있습니다. (책은 VirtualBox기준)
베이그런트? 사용자의 요구에 맞게 시스템 자원을 할당, 배치, 배포해 두었다가 필요 시 시스템을 사용할 수 있는 상태로 만들어 줌.(프로비저닝)
베이그런트 다운로드 : https://vagrantup.com/downloads.html
Vagrant by HashiCorp
Vagrant enables users to create and configure lightweight, reproducible, and portable development environments.
www.vagrantup.com
베이그런트 초기화
vagrant init
베이스 이미지가 없어서 오류 발생, 베이스 이미지 서치 해서 확인
https://app.vagrantup.com/boxes/search
https://app.vagrantup.com/centos/boxes/7
Vagrant Cloud by HashiCorp
Vagrant Cloud by HashiCorp
app.vagrantup.com
vagrant up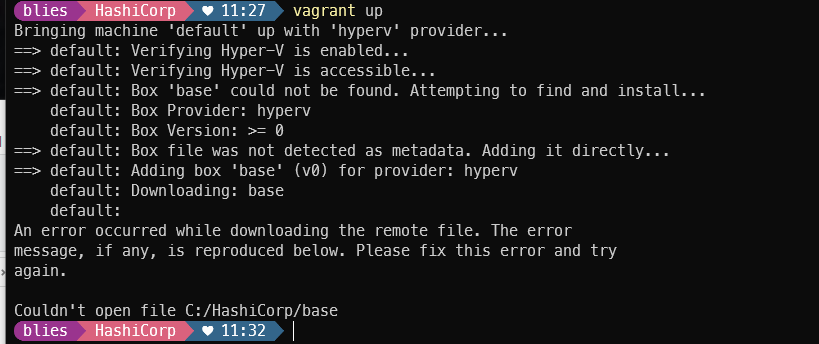
centos7을 사용할 예정이기 때문에 vagrantfile에서 config.vm.box = "centos/7" 로 변경
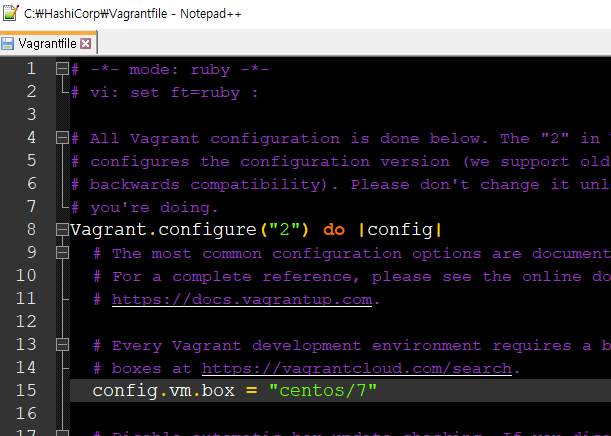
다시 vagrant up 후 정상적으로 설치중
책에서는 VirtualBox를 사용해서 혹시 hyper-v를 지원안하면 다시 해야하나 싶었는데 다행히 hyper-v도 정상적으로 지원하는것으로 확인, 스위치가 여러개 설정되있을 경우 중간에 선택해야 하는 과정 추가
vagrant up

정상적으로 켜진것으로 확인
ssh접속 후 uptime과 릴리즈 확인
vagrant ssh
uptime
cat /etc/*release*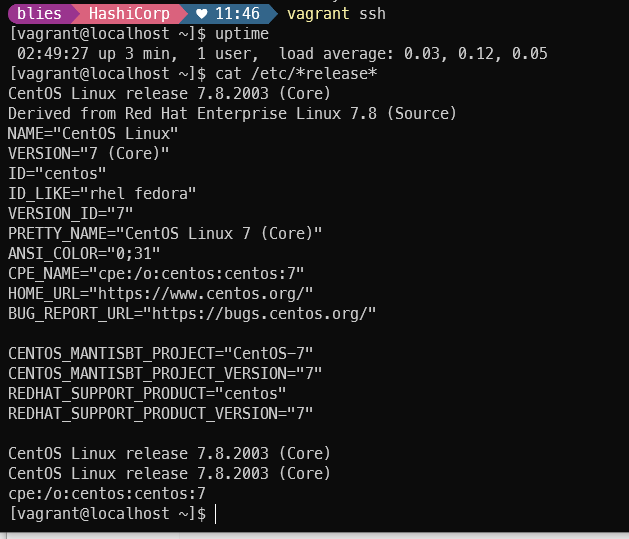
책 내용중 포트포워딩관련 에드온 설치가 필요한 것으로 나와있으나 Hyper-V의 경우 별도의 포트포워딩 없이 브릿시 네트워크 사용으로 바로 접속이 가능하여 별도의 포트포워딩 과정없이 진행.
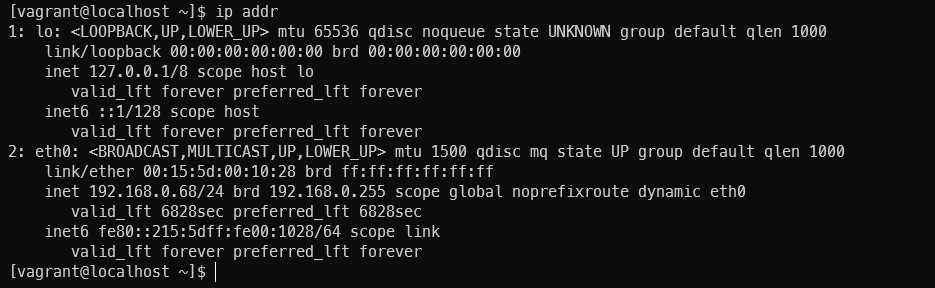
생성한 VM 삭제
vagrant destroy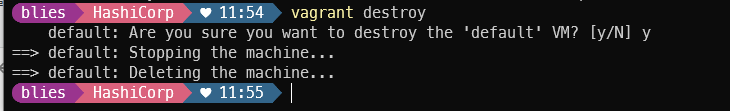
vagrantfile 설정시 참고,
provider 설정 시 hyperv가 먹히지 않아서 hyper-v로 설정했더니 정상적으로 작동
Learning to Use Vagrant on Windows 10
Vagrant and Hyper-V -- Tips and Tricks
Blog post that includes various tips, including how to install and use various features within Hyper-V.
docs.microsoft.com
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
#================#
# Ansible Server #
#================#
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.define "ansiable-server" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-Server"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-server"
cfg.vm.network "public_network"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
end
end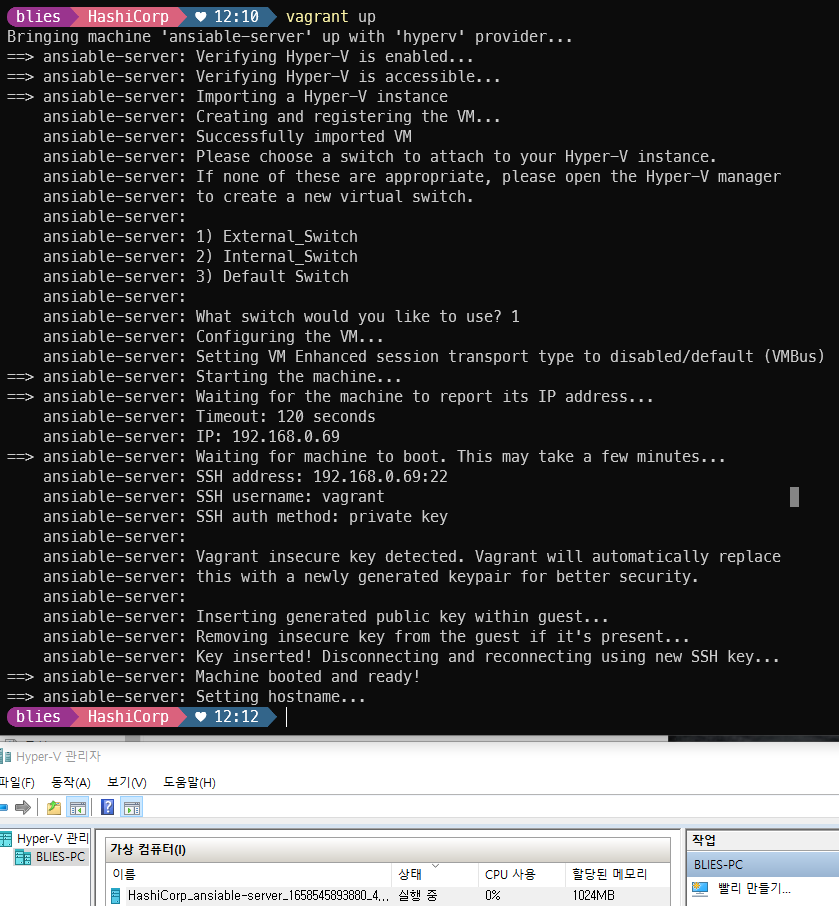
ssh 접속 시도, ansible 설치 확인, 종료
vagrant ssh
ansible
exit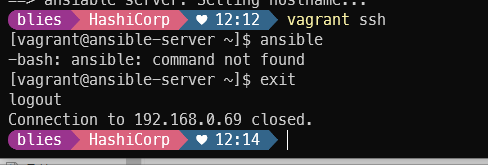
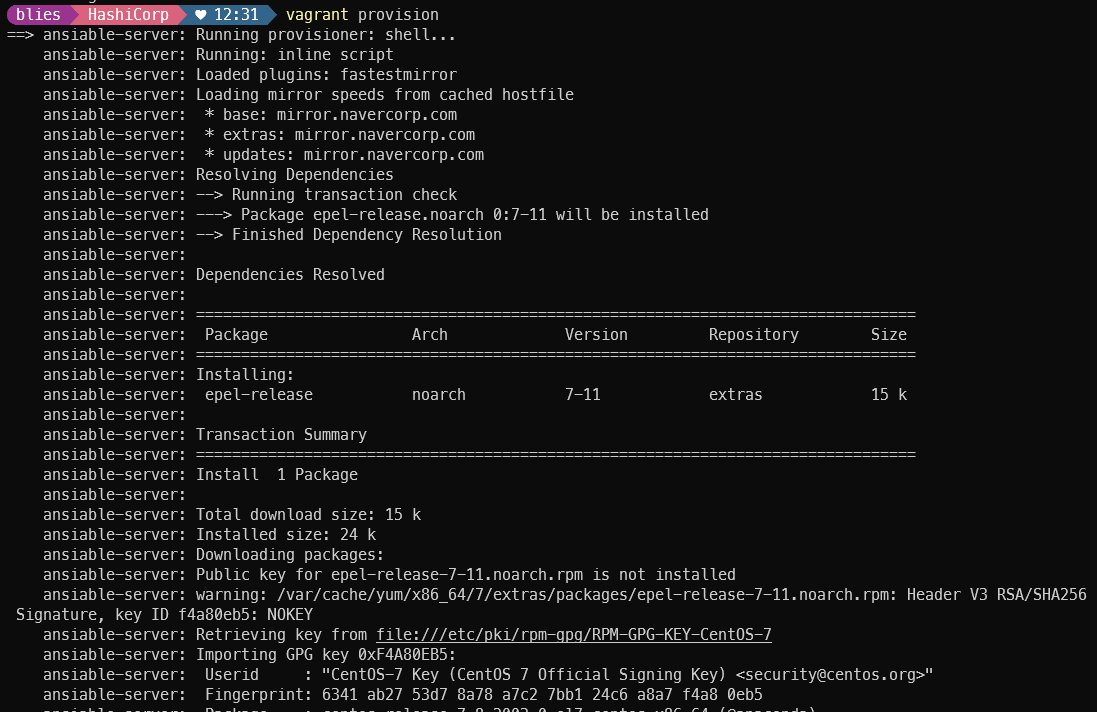
ansible no package 문제로 epel-release 추가
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
#================#
# Ansible Server #
#================#
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.define "ansiable-server" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-Server"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-server"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.70"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "yum install epel-release -y && yum install ansible -y"
end
end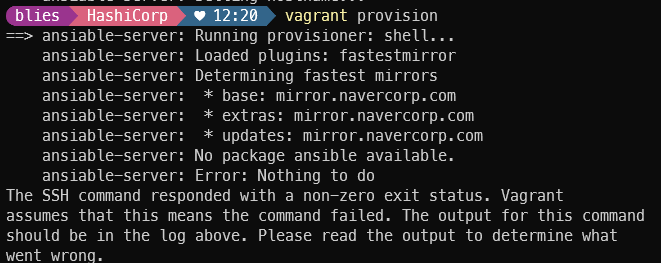
설치 후 정상 작동 확인
vagrant ssh
ansible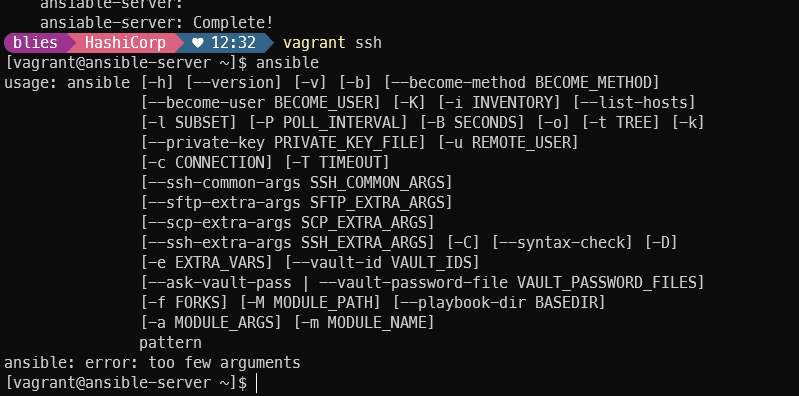
앤서블플레이북 실행환경 추가
yml 코드는 https://github.com/bjpublic/ansible
GitHub - bjpublic/ansible
Contribute to bjpublic/ansible development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
vagrantfile
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
#================#
# Ansible Server #
#================#
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.define "ansiable-server" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-Server"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-server"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.70"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "yum install epel-release -y && yum install ansible -y"
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ansible_env_ready.yml",
destination: "ansible_env_ready.yml"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "ansible-playbook ansible_env_ready.yml"
end
end
vagrant provision
vagrant ssh
ans
anp
vi ansible_env_ready.yml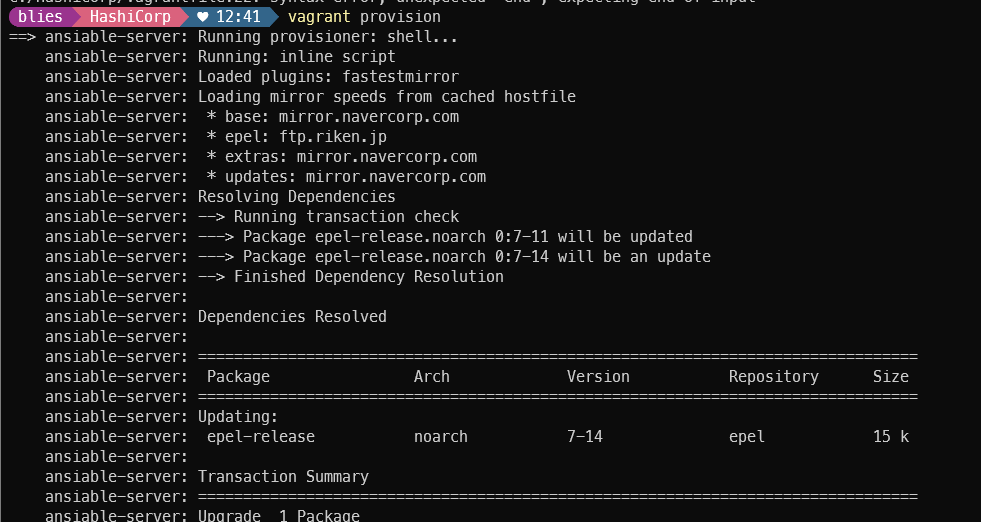
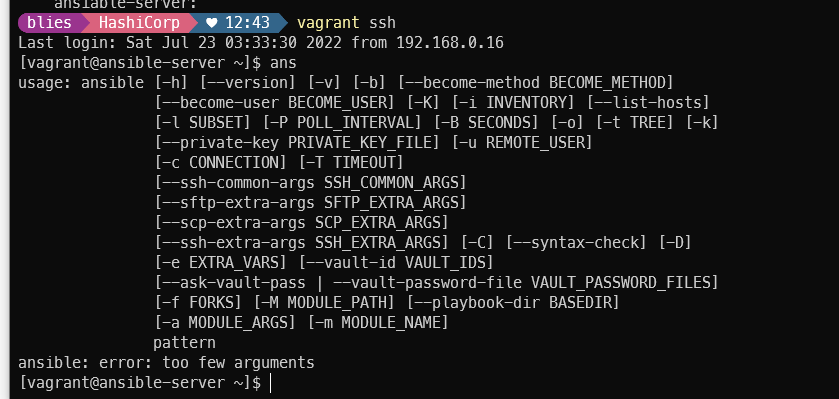
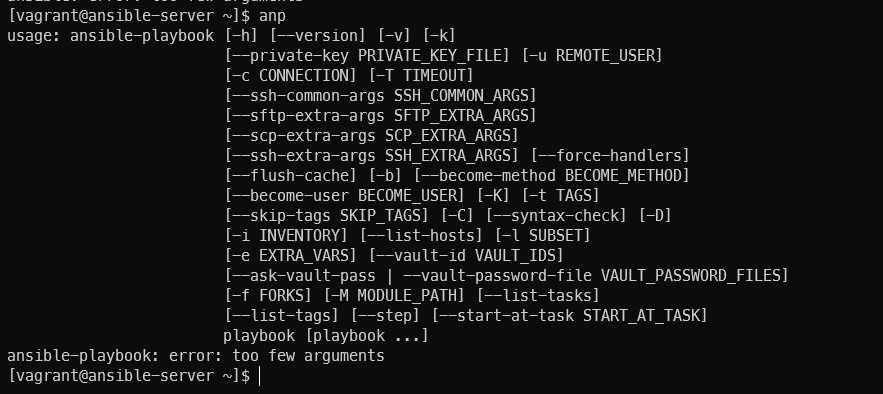
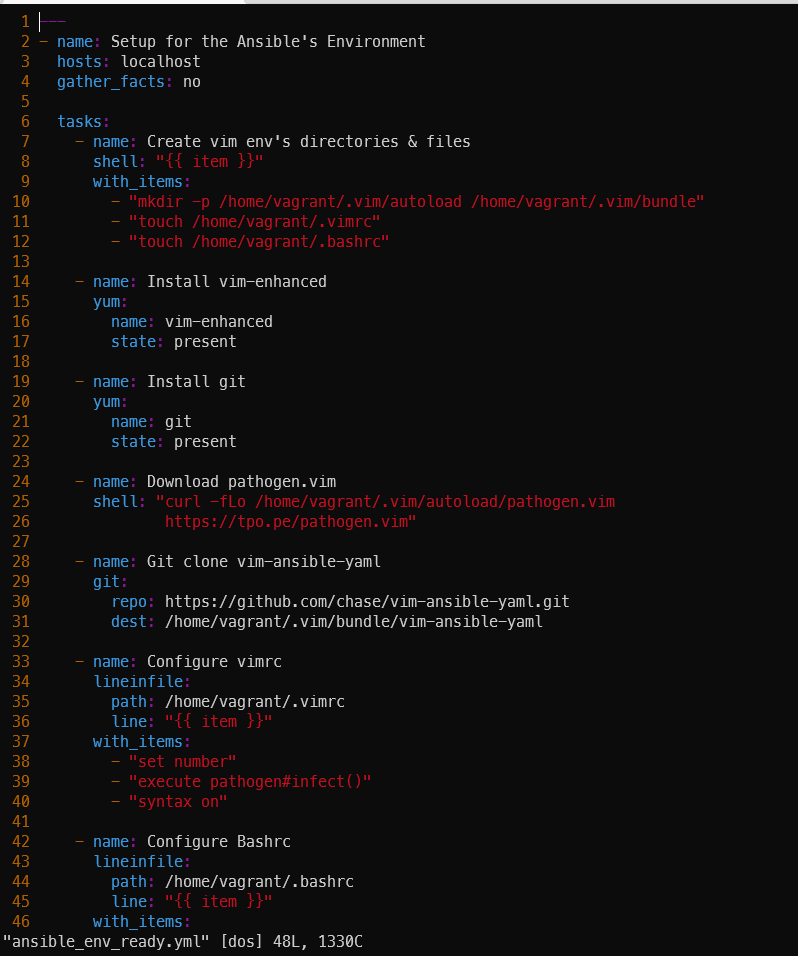
가상머신 강제 삭제
vagrant destroy -f
노드 추가한 코드 입력
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
#==============#
# CentOS nodes #
#==============#
#Ansible-Node01
config.vm.define "ansiable-node01" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node01"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node01"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.71", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
end
#Ansible-Node02
config.vm.define "ansiable-node02" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node02"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node02"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.72", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
end
#Ansible-Node03
config.vm.define "ansiable-node03" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node03"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node03"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.73", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
end
#================#
# Ansible Server #
#================#
config.vm.define "ansiable-server" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-Server"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-server"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.0.70", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "yum install epel-release -y && yum install ansible -y"
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ansible_env_ready.yml",
destination: "ansible_env_ready.yml"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "ansible-playbook ansible_env_ready.yml"
end
endvagrant up설치완료
접속 확인, 앤시아블은..넘어가도록 한다..
아이피를 설정해둔게 적용이 안되는것 같아서 설정을 변경(고정)
각 노드 별 아이피 설정 파일 생성
#!/bin/sh
#ip-node03
echo 'Setting static IP address for Hyper-V...'
cat << EOF > /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
DEVICE=eth0
BOOTPROTO=none
ONBOOT=yes
PREFIX=24
IPADDR=192.168.0.73
GATEWAY=192.168.0.1
DNS1=8.8.8.8
EOFdhcp로 잡히는걸 static ip로 변경 후에 네트워크 재시작(백그라운드에서 하지 않을 경우 넘어가지 않아서 백그라운드에서 시작)
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
#==============#
# CentOS nodes #
#==============#
#Ansible-Node01
config.vm.define "ansible-node01" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node01"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node01"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-node01.sh",
destination: "ip-node01.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-node01.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
end
#Ansible-Node02
config.vm.define "ansible-node02" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node02"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node02"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-node02.sh",
destination: "ip-node02.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-node02.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
end
#Ansible-Node03
config.vm.define "ansible-node03" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node03"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node03"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-node03.sh",
destination: "ip-node03.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-node03.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
end
#================#
# Ansible Server #
#================#
config.vm.define "ansible-server" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-Server"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-server"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-server.sh",
destination: "ip-server.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-server.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "yum install epel-release -y && yum install ansible -y"
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ansible_env_ready.yml",
destination: "ansible_env_ready.yml"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "ansible-playbook ansible_env_ready.yml"
end
end정상적으로 아이피 변경까지 확인
ansible_env_ready.yml 파일에 하기 내용 추가
---
- name: Setup for the Ansible's Environment
hosts: localhost
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: Add "/etc/ansible/hosts"
blockinfile:
path: /etc/ansible/hosts
block: |
[CentOS]
192.168.0.71
192.168.0.72
192.168.0.73vagrant ssh ansible-server
ans all -m ping
yes
yes
yes
ans all -m pink -k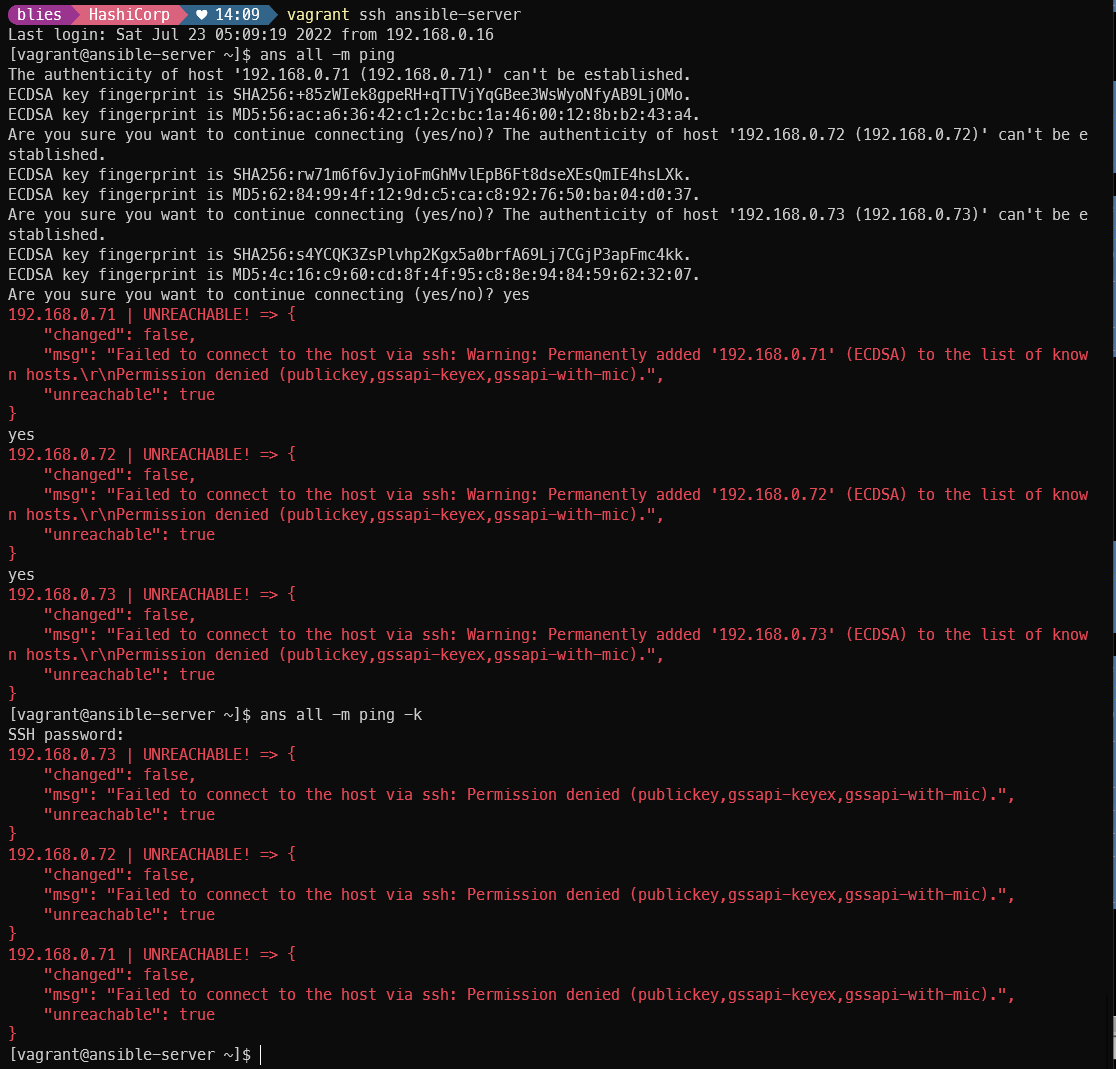
bash_ssh_confi_4_CentOS.sh파일
#! /usr/bin/env bash
now=$(date +"%m_%d_%Y")
cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config /etc/ssh_sshd_config_$now.backup
sed -i -e 's/PasswordAuthentication no/PasswordAuthentication yes/g' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
systemctl restart sshdVagrantfile
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
#==============#
# CentOS nodes #
#==============#
#Ansible-Node01
config.vm.define "ansible-node01" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node01"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node01"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-node01.sh",
destination: "ip-node01.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-node01.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "bash_ssh_conf_4_CentOS.sh"
end
#Ansible-Node02
config.vm.define "ansible-node02" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node02"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node02"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-node02.sh",
destination: "ip-node02.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-node02.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "bash_ssh_conf_4_CentOS.sh"
end
#Ansible-Node03
config.vm.define "ansible-node03" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-node03"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-node03"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-node03.sh",
destination: "ip-node03.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-node03.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "bash_ssh_conf_4_CentOS.sh"
end
#================#
# Ansible Server #
#================#
config.vm.define "ansible-server" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "centos/7"
cfg.vm.provider "hyper-v" do |hv|
hv.name = "Ansible-Server"
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "ansible-server"
cfg.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "External_Switch"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ip-server.sh",
destination: "ip-server.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "source ./ip-server.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "systemctl restart network &"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "yum install epel-release -y && yum install ansible -y"
cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ansible_env_ready.yml",
destination: "ansible_env_ready.yml"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "ansible-playbook ansible_env_ready.yml"
end
end정상 핑 확인
vagrant provision
vagrant ssh ansible-server
ans all -m pingg -k
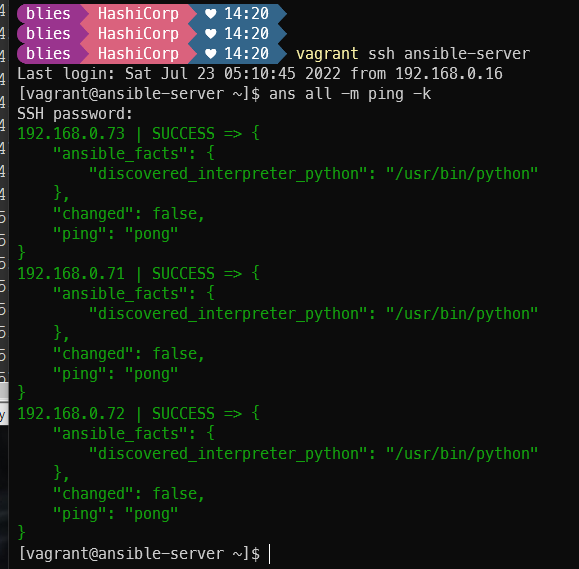
ansible_env_ready.yml
---
- name: Setup for the Ansible's Environment
hosts: localhost
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: Add "/etc/ansible/hosts"
blockinfile:
path: /etc/ansible/hosts
block: |
[CentOS]
192.168.0.71
192.168.0.72
192.168.0.73
- name: Install sshpass for Authentication
yum:
name: sshpass
state: present
- name: Create vim env's directories & files
shell: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "mkdir -p /home/vagrant/.vim/autoload /home/vagrant/.vim/bundle"
- "touch /home/vagrant/.vimrc"
- "touch /home/vagrant/.bashrc"
- name: Install vim-enhanced
yum:
name: vim-enhanced
state: present
- name: Install git
yum:
name: git
state: present
- name: Download pathogen.vim
shell: "curl -fLo /home/vagrant/.vim/autoload/pathogen.vim
https://tpo.pe/pathogen.vim"
- name: Git clone vim-ansible-yaml
git:
repo: https://github.com/chase/vim-ansible-yaml.git
dest: /home/vagrant/.vim/bundle/vim-ansible-yaml
- name: Configure vimrc
lineinfile:
path: /home/vagrant/.vimrc
line: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "set number"
- "execute pathogen#infect()"
- "syntax on"
- name: Configure Bashrc
lineinfile:
path: /home/vagrant/.bashrc
line: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "alias ans='ansible'"
- "alias anp='ansible-playbook'"known_hosts 자동등록
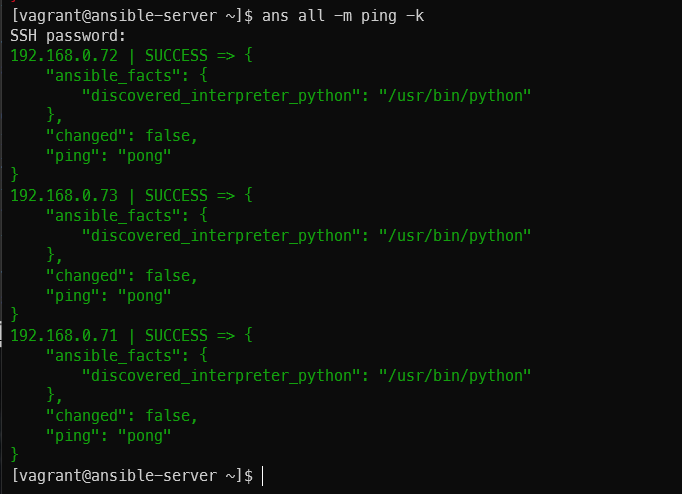
[우아하게 앤서블] Chapter 2 - 앤서블 체험하기
책에서는 Virtual Box로 진행하였으나, 기존 Hyper-V 테스트 환경이 있어서 Hyper-V에서 진행하며,
기존 가지고 있던 CentOS7 VM파일을 내보내기 하여 구성 진행
각 호스트 네임 및 아이피 설정 작업 진행
| Hostname | IP |
| ansible-server | 192.168.0.170 |
| ansible-node01 | 192.168.0.171 |
| ansible-node02 | 192.168.0.172 |
| ansible-node03 | 192.168.0.173 |
설정 후 인터넷이 한대밖에 안되는 증상이 있어서 확인 결과 MAC주소를 정적으로 설정 해둔 부분이 문제여서 해당 부분 동적으로 변경 후 정상 통신 확인
yum install ansible -y를 실행하였으나 No package ansible available 노출
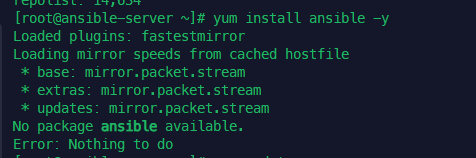
구글링 해보니 No package가 뜰경우
yum install epel-release명령어 진행 후에 진행 하는 것으로 확인하였고 설치완료
yum install ansible -y
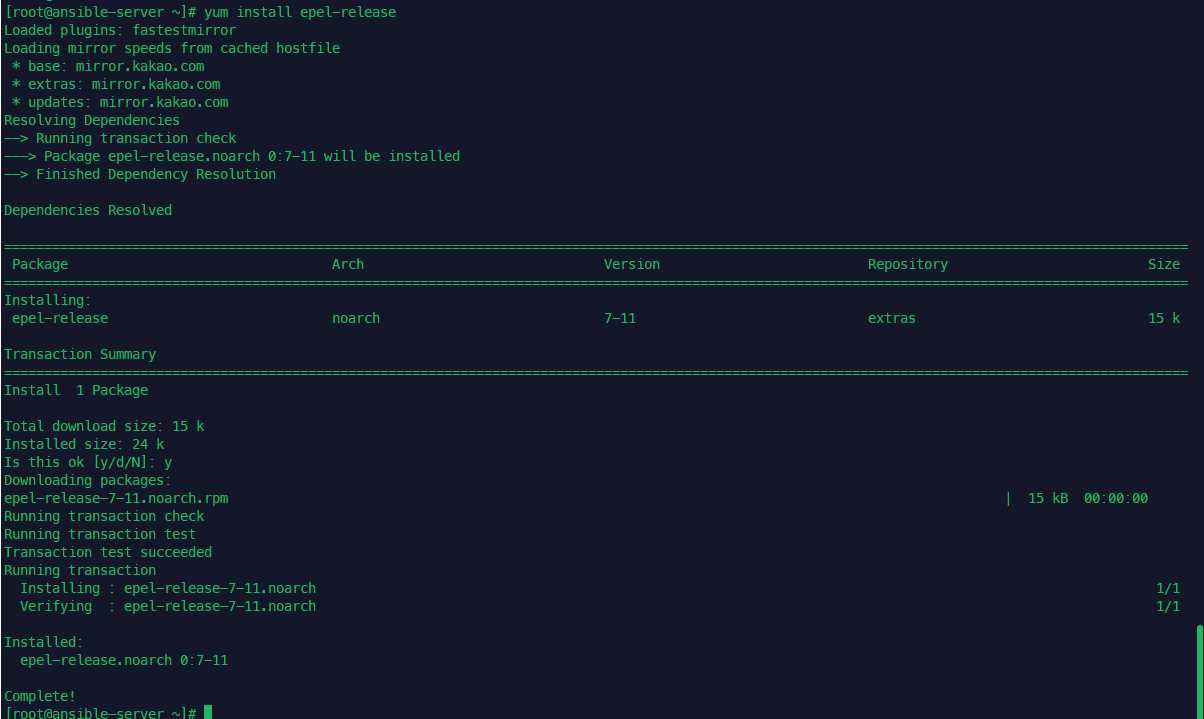
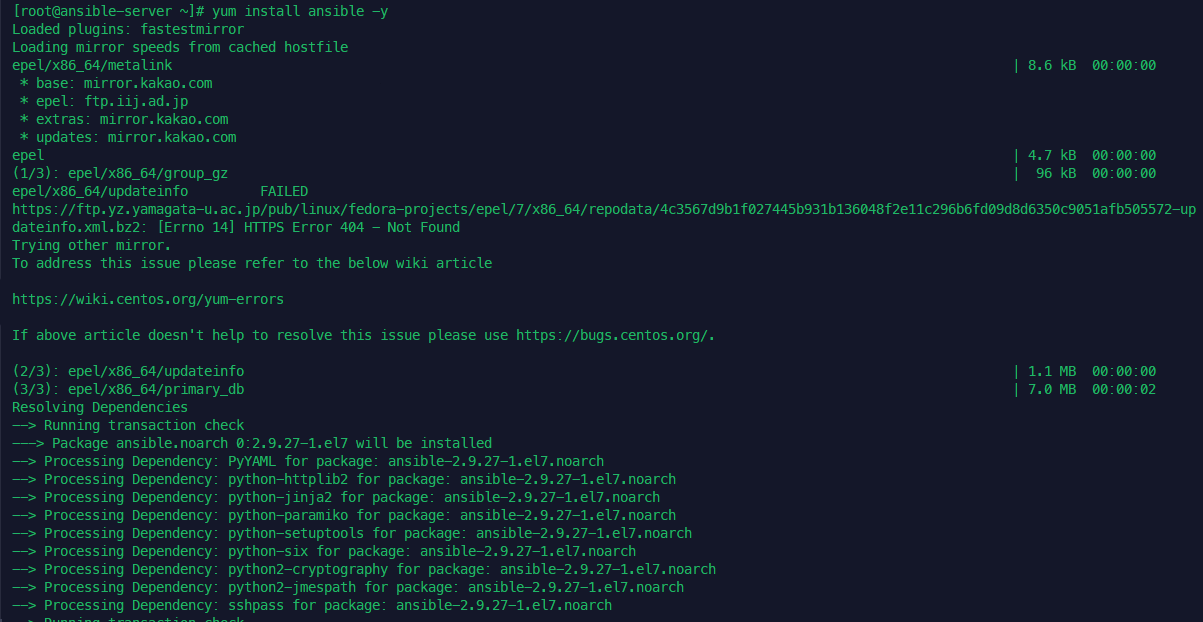
앤서블 사용 가능한 명령어 확인
ls /usr/bin/ansible*
노드 호스트 추가
echo "192.168.0.171" >> /etc/ansible/hosts
echo "192.168.0.172" >> /etc/ansible/hosts
echo "192.168.0.173" >> /etc/ansible/hosts
# check host
cat /etc/ansible/hosts | grep -v "^#"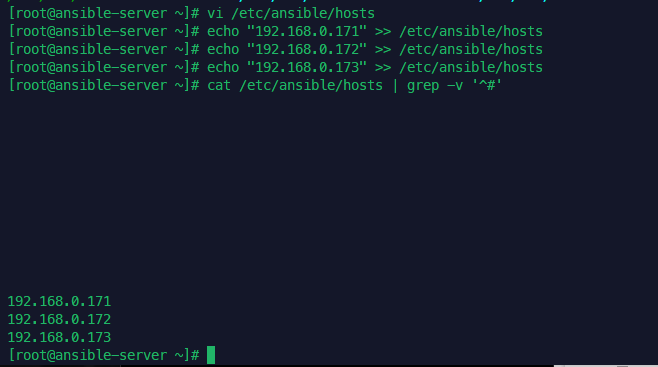
known_hosts_key값 입력 -> 노드 숫자만큼 yes입력
ansible all -m ping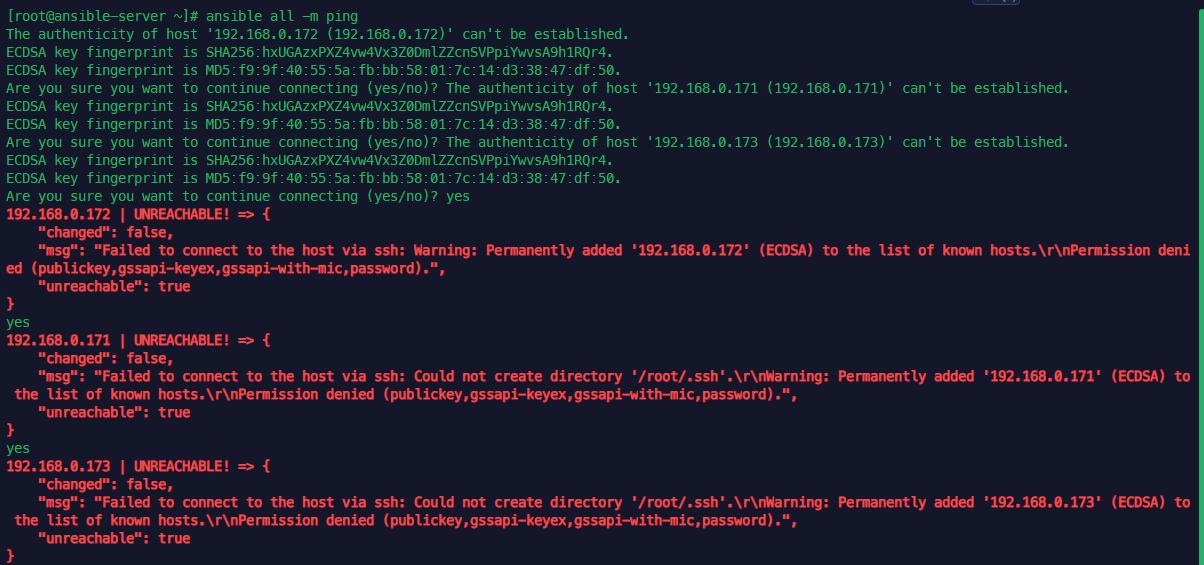
앤서블 명령이 정상적으로 입력되는지 확인
ansible all -m ping -k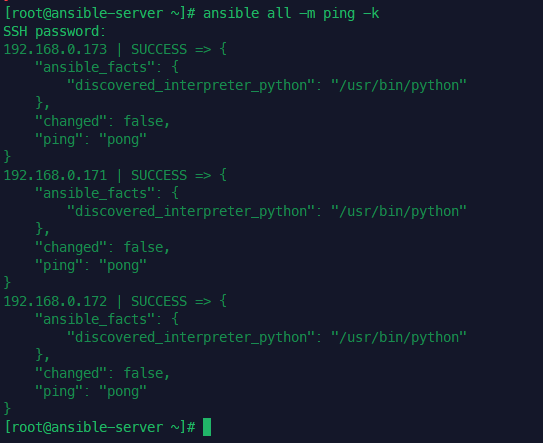
앤서블 설정파일
cat /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
/etc/ansible/hosts 파일에서 노드 설정 시 alias 설정이 가능
all 입력시 모드 노드들 지정
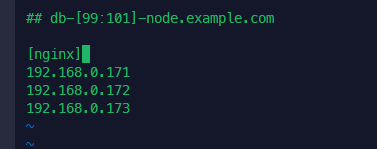
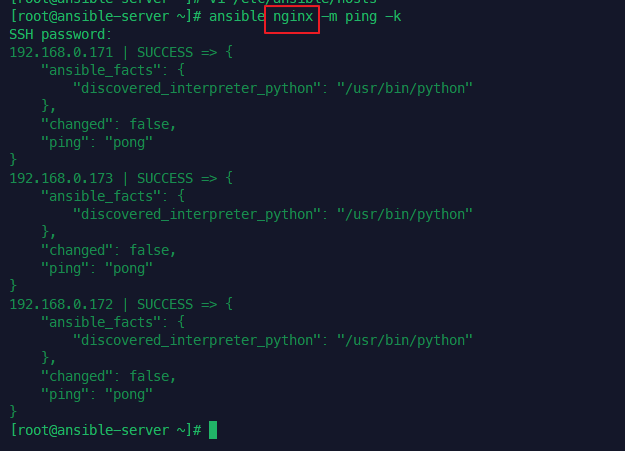
앤서블 실행 시 사용할 수 있는 옵션 값
| 옵션 | 풀 네임 | 네용 |
| -i | --inventory-file | 적용될 노드들을 선택 |
| -m | --odule-name | 사용하는 모듈 |
| -k | --ask-pass | 암호를 물어보는 설정 |
| --list-hosts | 적용되는 노드들을 확인 |
특정 노드에만 ping 명령
echo "192.168.0.171" >> customized_inven.lst
echo "192.168.0.172" >> customized_inven.lst
cat customized_inven.lst
ansible -i customized_inven.lst all -m pink -k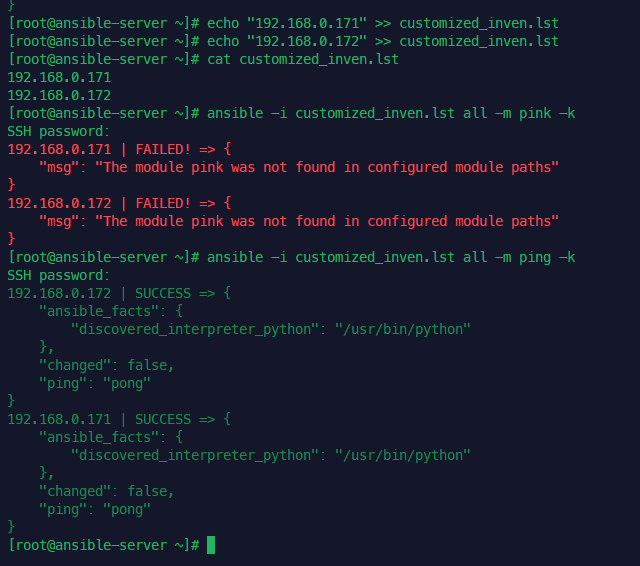
특정 노드에 실행
ansible -i customized_inven.lst 192.168.0.171 -m ping -k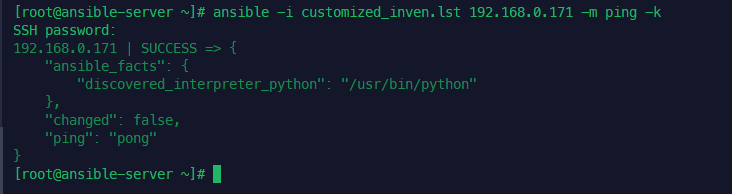
적용노드 파악(실제로 실행되지 않음
ansible all -m ping -k --list-hosts
ansible all -m ping --list-hosts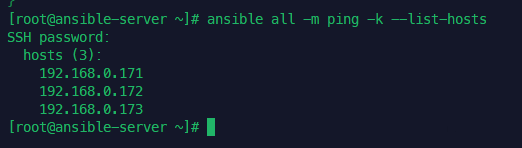
-m 을 사용하는 모듈, shell 명령 사용시 bash쉘에서 사용하는것과 동일하게 사용 가능, -a를 넣어서 인자값을 넣을 수 있음
-m shell 명령이 기본이기 때문에 생략할 수 있으나 명시성을 높이기 위해 기입하는 것을 추천
ansible all -m shell -a "uptime" -k
ansible all -a "uptime" -k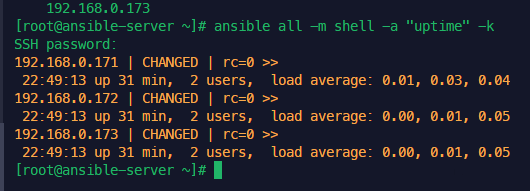
ansible all -m shell -a "df -h" -k
ansible all -m shell -a "free -h" -k
user 모듈
사용자 추가
ansible all -m user -a "name=bjpublic" -k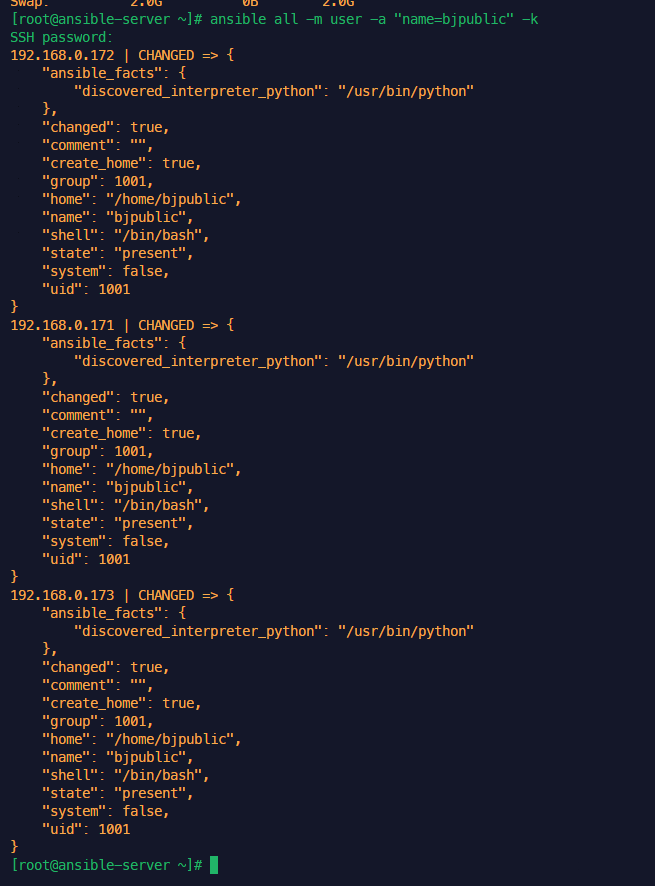
추가 확인
ansible all -m shell -a "tail -n 1 /etc/passwd" -k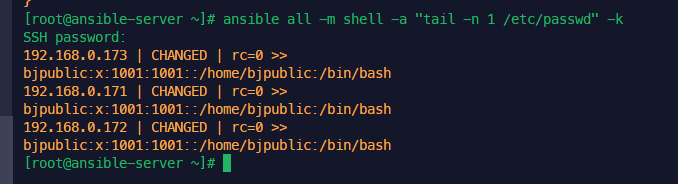
삭제
ansible all -m user -a "name=bjpublic state=absent"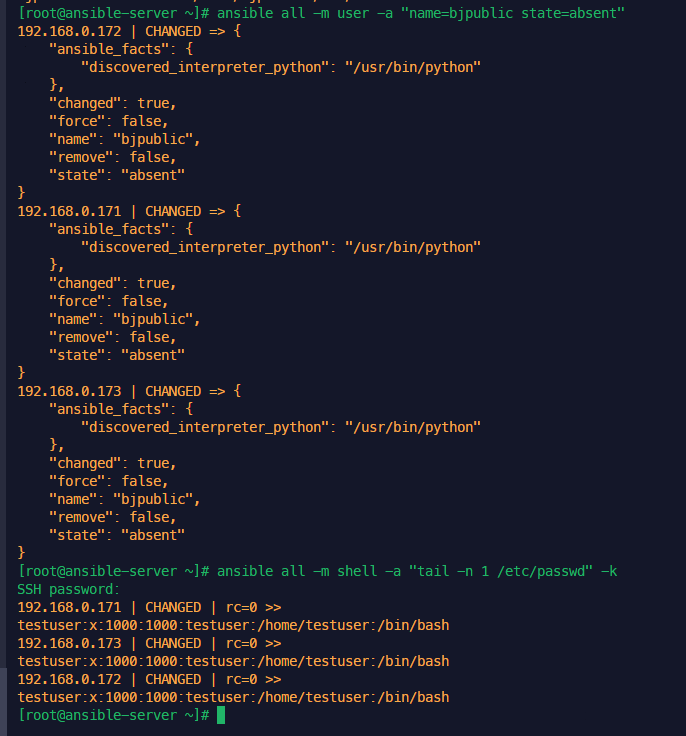
yum : 패키지 설치
"name=<패키지이름> state=<상태>" present 설치, absent 삭제
ansible all -m yum -a "name=httpd state=present" -k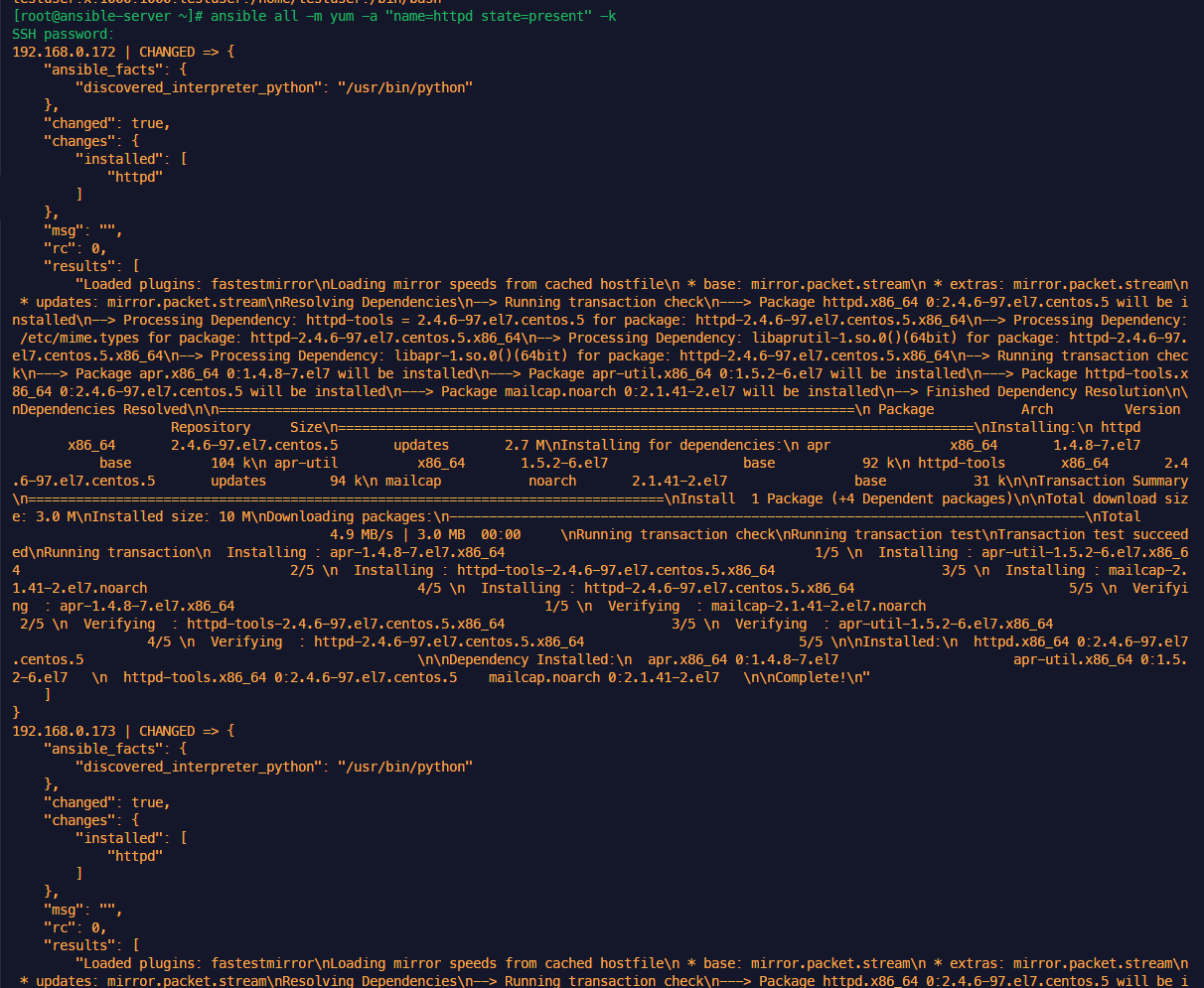
copy : 파일을 원격지로 복사
"src=<보낼파일의 위치와 이름> dest=<받을 파일의 위치와 이름>"
기본페이지 다운로드
curl https://httpd.apache.org -o index.html
index.html 노드로 이동
ansible all -m copy -a "src=index.html dest=/var/www/html/index.html" -k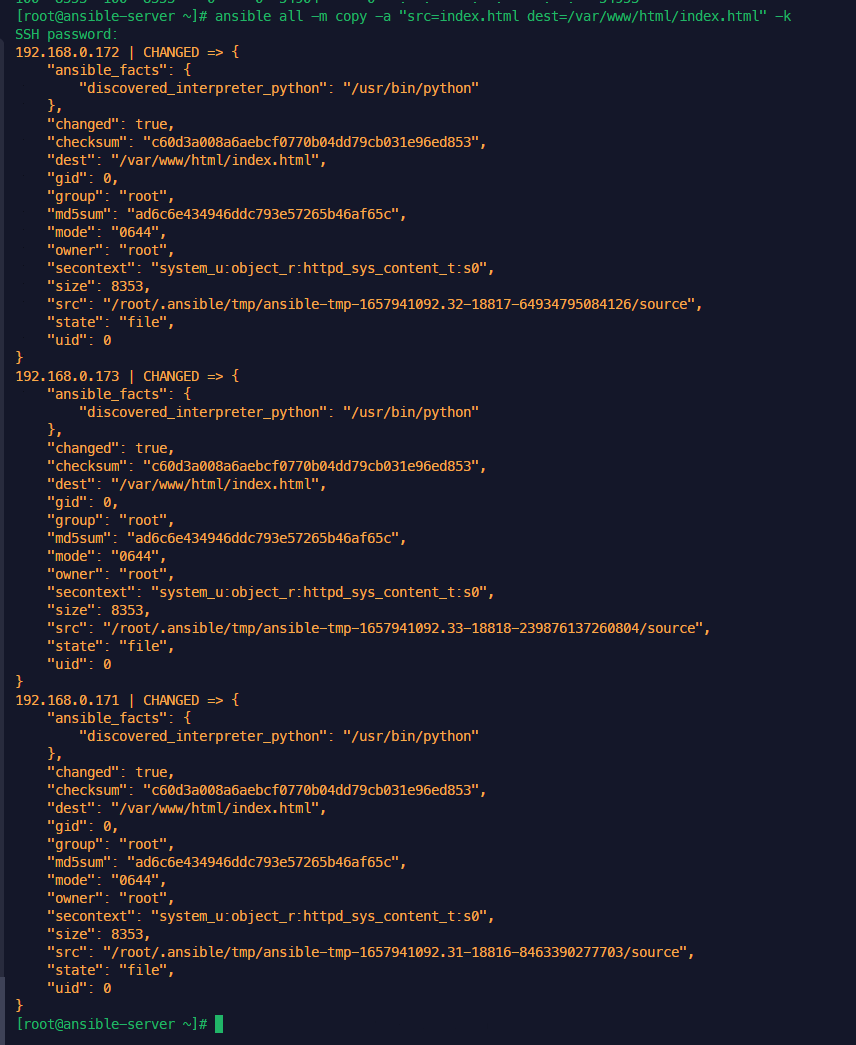
service : 서비스 관리, 방화벽 OFF
ansible all -m service -a "name=httpd state=started" -k
ansible all -m shell -a "systemctl stop firewalld" -k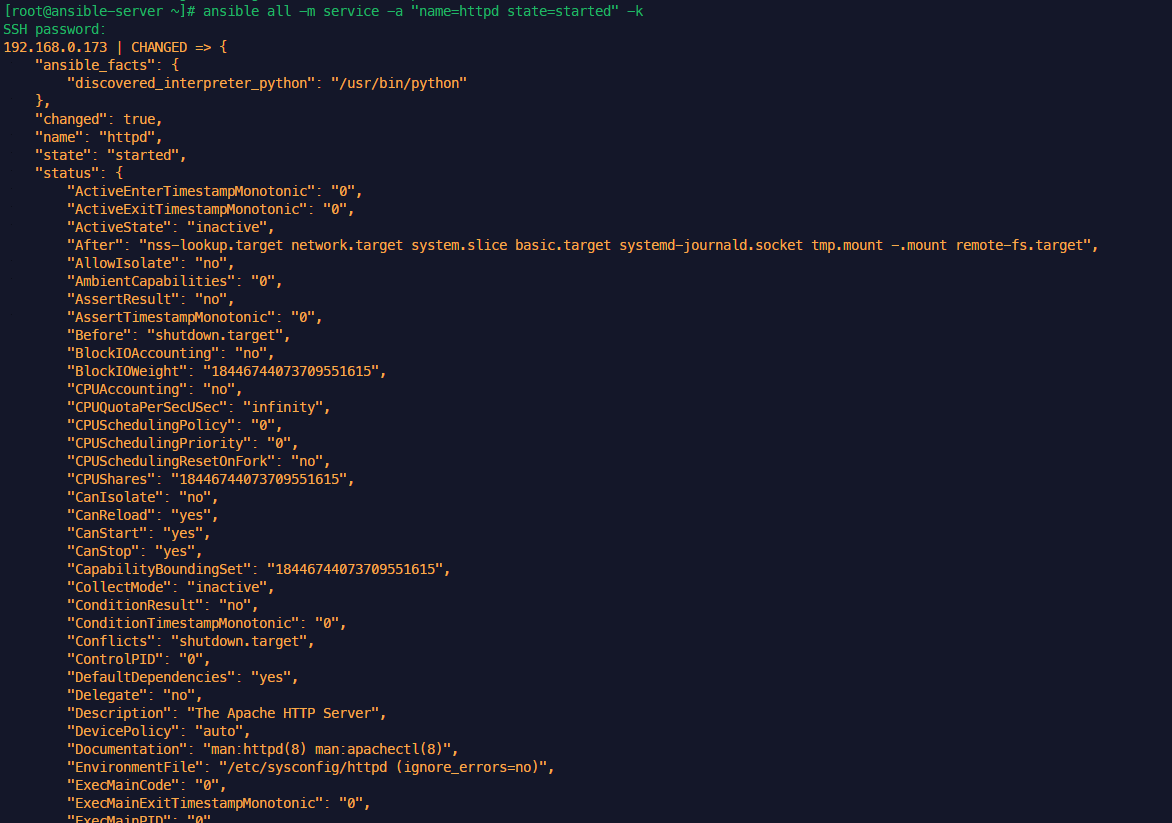
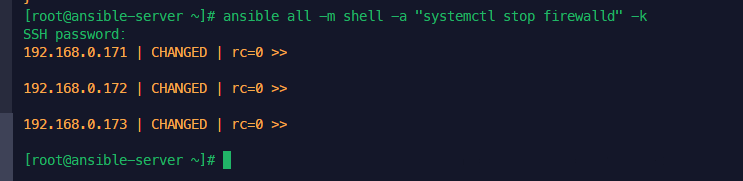
웹서버 작동 확인

웹서버 삭제 진행
ansible all -m yum -a "name=httpd state=absent" -k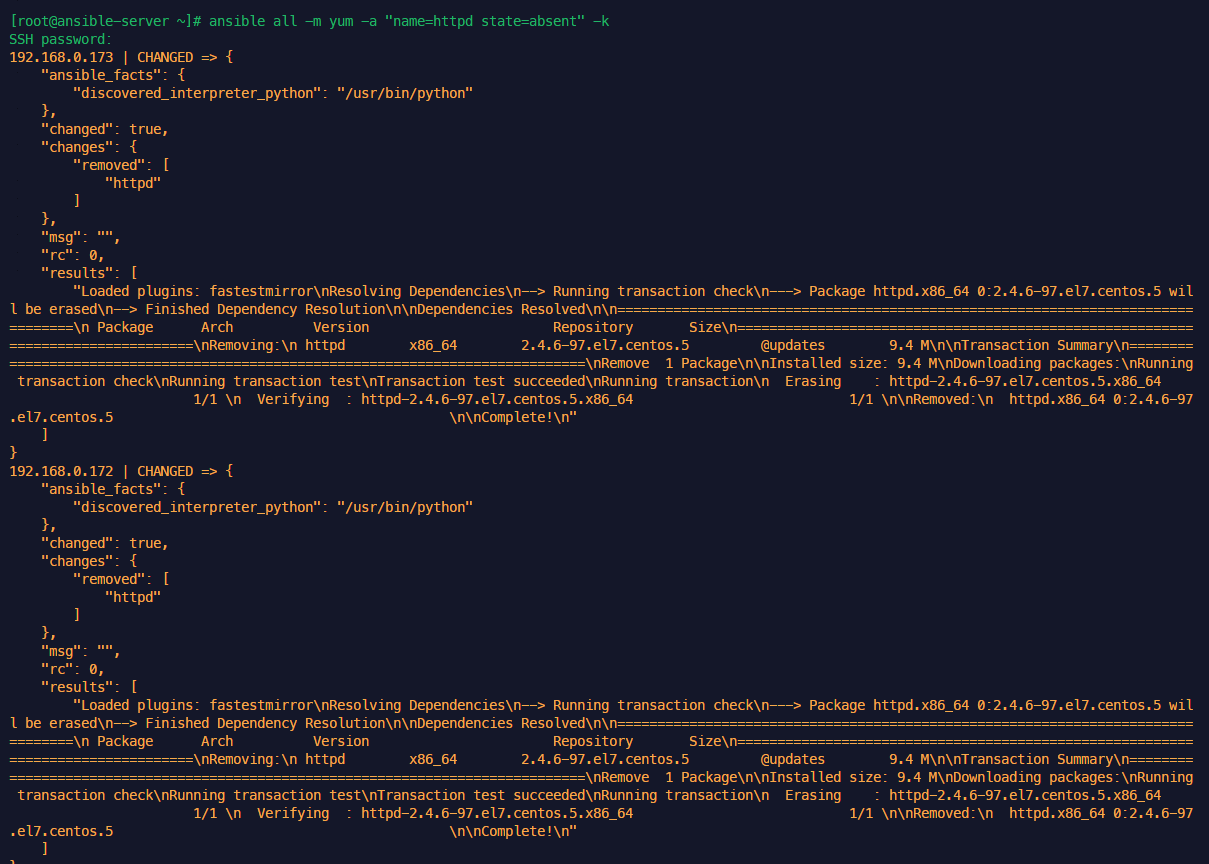
작업할 내용을 파일로 작성(playbook)
멱등성 : 연산을 여러 번 적용하더라도 결과가 달라지지 않는 성질
3번 노드를 2번 추가
echo로 한경우 두줄이 추가되나 ansible로 할 경우 1개만 추가됨(멱등성)
echo "192.168.0.173" >> customized_inven.lst
echo "192.168.0.173" >> customized_inven.lst
ansible localhost -c local -m lineinfile -a "path=customized_inven.lst line=192.168.0.174"
ansible localhost -c local -m lineinfile -a "path=customized_inven.lst line=192.168.0.174"
cat customized_inven.lst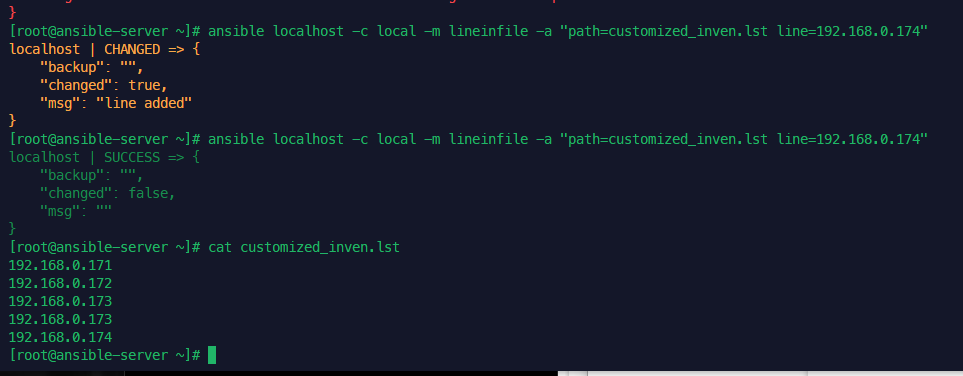
플레이북은 앤서블 플레이북(ansible-playboo)이라는 파일로 실행
nginx_install.yml 생성
---
- name: Install nginx on linux
hosts: nginx
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: install epel-release
yum: name=epel-release state=laste
- name: install nginx web server
yum: name=nginx state=present
- name: upload default index.html for web server
get_url: url=https://www.nginx.com dest=/usr/share/nginx/html/ mode=0644
- name: start nginx web server
service: name=nginx state=startedansible-playbook nginx_install.yml -k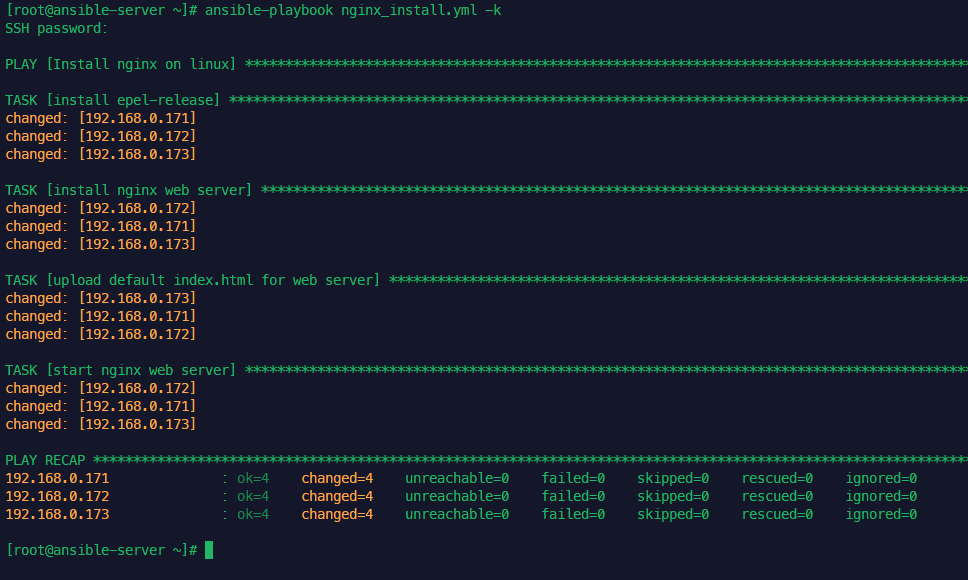
사이트 정상 작동 확인

Windows Server (2012 R2,2016, 2019) KMS Key Change Script
redplug 입니다.
Windows Server에 인증키 값을 MAK -> KMS 변경이 필요한 경우에 사용하는 스크립트 입니다.
Azure VM 인 경우 Azure KMS사용을 위하여 $AzureKMSUser 활성
2012 R2의 경우 get-computerinfo 명령어가 없어 systeminfo 값을 활용하여 체크 합니다.
하기 기입된 KMS키는 MS Docs에 공개된 KMS용 Client키(KMS 인증을 받기 위해 적용하는 키) 입니다.
# kmscheck.ps1
아래 코드를 긁어서 할 경우 정상적으로 불러오지 못하는 경우가 있어 첨부된 파일을 사용부탁드립니다.
|
# kmscheck.ps1
# Windows 2012, 2012 R2, 2016, 2019 KMS Key Change and activation Script
# Windows use on Auzre, AzureKMSUse setting 1
# KeyCheckMode is just check KMS Key Serial, not change key and activation
# Windows KMS Client key is public. url : https://docs.microsoft.com/ko-kr/windows-server/get-started/kms-client-activation-keys
# Options
$KeyCheckMode = 1 # 1=True, 0=False
$AuzreKMSUse = 1 # 1=True, 0=False
$WS2012Check_en = systeminfo | Select-String -pattern "OS Name:"
$WS2012Check_kr = systeminfo | Select-String -pattern "OS 이름:"
if ( $WS2012Check_en -eq $null) {
$OSLang = "kr"
$WS2012Check = $WS2012Check_kr
}
else {
$OSLang = "en"
$WS2012Check = $WS2012Check_en
}
if ( $WS2012Check -like "*Microsoft Windows Server 2012*") {
switch ( $OSLang ) {
'en' {
$OsName = $WS2012Check -creplace 'OS Name:', ''
}
'kr' {
$OsName = $WS2012Check -creplace 'OS 이름:', ''
}
}
$OsName = $OsName.TrimStart()
}
else {
$OsName = (get-computerinfo).OsName
}
# Windows Version Edition Check
Write-Host "OSName : ", $OsName
switch ( $OsName ) {
# Windows Server 2012
'Microsoft Windows Server 2012' {
$kmskey = "BN3D2-R7TKB-3YPBD-8DRP2-27GG4"
}
'Microsoft Windows Server 2012 Standard' {
$kmskey = "XC9B7-NBPP2-83J2H-RHMBY-92BT4"
}
'Microsoft Windows Server 2012 Datacenter' {
$kmskey = "48HP8-DN98B-MYWDG-T2DCC-8W83P"
}
# Windows Server 2012 R2
'Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard' {
$kmskey = "D2N9P-3P6X9-2R39C-7RTCD-MDVJX"
}
'Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter' {
$kmskey = "W3GGN-FT8W3-Y4M27-J84CP-Q3VJ9"
}
'Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials' {
$kmskey = "KNC87-3J2TX-XB4WP-VCPJV-M4FWM"
}
# Windows Server 2016
'Microsoft Windows Server 2016 Datacenter' {
$kmskey = "CB7KF-BWN84-R7R2Y-793K2-8XDDG"
}
'Microsoft Windows Server 2016 Standard' {
$kmskey = "WC2BQ-8NRM3-FDDYY-2BFGV-KHKQY"
}
'Microsoft Windows Server 2016 Essentials' {
$kmskey = "JCKRF-N37P4-C2D82-9YXRT-4M63B"
}
# Windows Server 2019
'Microsoft Windows Server 2019 Datacenter' {
$kmskey = "WMDGN-G9PQG-XVVXX-R3X43-63DFG"
}
'Microsoft Windows Server 2019 Standard' {
$kmskey = "N69G4-B89J2-4G8F4-WWYCC-J464C"
}
'Microsoft Windows Server 2019 Essentials' {
$kmskey = "WVDHN-86M7X-466P6-VHXV7-YY726"
}
}
if ( $KeyCheckMode -eq 0 ) {
if ( $AuzreKMSUse -eq 1 ) {
write-host "### KMS Server Change (Azure)"
Invoke-Expression "$env:windir\system32\cscript.exe $env:windir\system32\slmgr.vbs /skms kms.core.windows.net:1688"
}
write-host "### Insert KMS Key"
Invoke-Expression "$env:windir\system32\cscript.exe $env:windir\system32\slmgr.vbs /ipk $kmskey"
write-host "### KMS Key Activation"
sleep 10
Invoke-Expression "$env:windir\system32\cscript.exe $env:windir\system32\slmgr.vbs /ato"
Read-Host -Prompt "Press any key to continue"
}
else {
write-host ""
write-host "#########################################################"
write-host "########### KEY CHECK MODE ###########"
write-host "########### KMS NOT ACTIVATE, JUST KEY CHECK ###########"
write-host "#########################################################"
write-host "OSName : " $OsName
write-host "KMS Key : " $kmskey
}
|
[Scripts] 리눅스 버젼 체크
리눅스 버젼 체크용 스크립트
Ubuntu, CentOS 및 특정 버젼에 대한 체크 목적으로 사용
Major 및 Minor까지 체크 가능
|
OSVersionCheck()
{
OSDistribution=$(cat /etc/*release*)
if [[ "$OSDistribution" == *Ubuntu* ]];then
ubuntuVer=$(lsb_release -r | awk '{print $2}')
if [ -z "$ubuntuVer" ];then
echo '### cannot see ubuntu version, manual check ver, and script exit'
exit
fi
case $ubuntuVer in
# ubuntu 12.04 ~ 16.04
12.04* | 14.04* | 16.04*)
echo "Ubuntu 12.04, 14.04, 16.04"
;;
# ubuntu 18.04 ~ 20.04
18.04* | 20.04*)
echo "Ubuntu 18.04, 20.04"
;;
*)
echo "Ubuntu but Untested OS"
esac
elif [[ "$OSDistribution" == *CentOS* ]];then
RHELVer=`cat /etc/redhat-release |awk '{print $3}'`
if [ "$RHELVer" = "release" ];then
RHELVer=`cat /etc/redhat-release |awk '{print $4}'`
fi
case $RHELVer in
# CentOS 6.0 ~ 6.3
6.0 | 6.1 | 6.2 | 6.3)
echo "CentOS 6.0 ~ 6.3"
# CentOS 6.4 ~ 6.10
;;
6.4 | 6.5 | 6.6 | 6.7 | 6.8 | 6.9 | 6.10)
echo "CentOS 6.4 ~ 6.10"
;;
# CentOS 7.X
7.*)
echo "CentOS 7.XX"
;;
*)
echo "CentOS but Untested OS"
esac
else
echo "Untested OS, not centOS Ubuntu"
fi
}
OSVersionCheck
|
